探索不同的土木工程项目
微信号|公路展望
微信又改版了
很多新朋友都说找不到陆先生
点击顶部“道路视图”→点击右上角“...”→点击“设为星级★”
为“Road Watch”添加一颗星星,这样您就不会错过它!
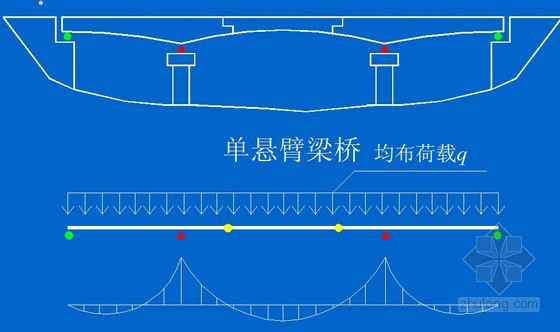
为了满足桥面变形的要求,通常在两梁端之间、梁端与桥台之间或桥梁铰接处设置伸缩缝。 伸缩缝要求能在平行和垂直于桥梁轴线两个方向自由伸缩,且坚固可靠。 车辆行驶时应平稳,无突然跳动和杂音; 能够防止雨水、垃圾渗入、堵塞; 安装、检查、维护、清除污垢必须简单、方便。 设置伸缩缝的地方,必须断开栏杆和桥面铺装。
膨胀节概述
桥梁伸缩缝简介
桥梁伸缩缝的作用是调节车辆荷载引起的上部结构与桥梁建筑材料之间的位移和连接。 斜交桥的伸缩装置一旦损坏,将严重影响行车的速度、舒适性和安全性,甚至造成行车安全事故。
膨胀节功能:
桥梁伸缩尺寸长期暴露在大气中,使用环境比较恶劣。 它们是桥梁结构中最容易损坏、最难修复的部位。 桥梁伸缩缝的破坏可能会造成较大的车辆冲击载荷,使行车条件恶化,引起车辆跳动、噪声、漏水,影响行车安全,大大缩短桥梁的使用寿命。
膨胀节功能缺失或损坏的危险:
伸缩缝型号
桥梁伸缩缝型号有:GQF-C型、GQF-Z型、GQF-E型、GQF-F型、GQF-MZL型,均为采用热轧一体成型异型钢设计的桥梁伸缩缝产品。
其中GQF-C型、GQF-Z型、GQF-L型、GQF-F型桥梁伸缩装置适用于伸缩量小于80mm的桥梁。
GQF-MZL桥梁伸缩缝装置是由边梁、中心梁、横梁和连杆机构组成的组合式桥梁伸缩缝装置。 适用于伸缩量80mm-1200mm的大中跨桥梁。
代码表示方法与中华人民共和国交通运输行业标准表示方法一致。
,以GQF-C60、GQF-F80、GQF-MZL480、GQF-C60(NR)、GQF-F80(CR)为例。
GQF是交通运输行业标准中规定的伸缩缝装置代号。
型号代号:-MZL表示模块化型、直梁连杆链条型:
(C、Z、F、L、)代表异型钢的形状。
伸缩装置位移数字表示:0-1200mm
NR和CR代表橡胶类型:NR代表天然橡胶,CR代表氯丁橡胶
膨胀节类型
无缝类型:暗缝式(连续桥面,TST)
对接型式:填充对接型、嵌入对接型(仿毛型)
钢支撑型式(梳板)
组合形式:橡胶板式
模块类型:毛雷尔型
无缝的
无缝伸缩装置是当接缝结构不伸出桥面时。 桥端部伸缩间隙内填充弹性材料,并铺设防水材料。 然后将粘弹性复合材料铺设在桥面铺装层上,使桥面铺装与伸缩缝处路面形成连续体。 节点处沥青混凝土、弹塑性等材料的变形吸收梁的伸缩,同时为车轮提供支撑结构。 常见形式有连续桥面、TST碎石弹性伸缩缝等。
此类伸缩装置的主要特点是:①能适应桥梁上部结构的伸缩变形和少量旋转变形; ②桥面铺装形成连续体,行驶时不产生冲击或振动,行驶舒适性好; ③伸缩装置本身形成多重防水结构,具有良好的防水性能; ④ 在寒冷地区,易于机械化除雪和维护,且不损伤接缝; ⑤ 施工简单,易于维护和更换。此类伸缩装置通常是在路面(桥面)施工完成后,用切割机切割路面,在槽口内注入填缝材料进行施工。 。 只适用于热胀冷缩小的零件(一般
严格按照工艺要求安装的无缝伸缩缝粘结材料的使用寿命约为一般改性沥青路面的两倍。

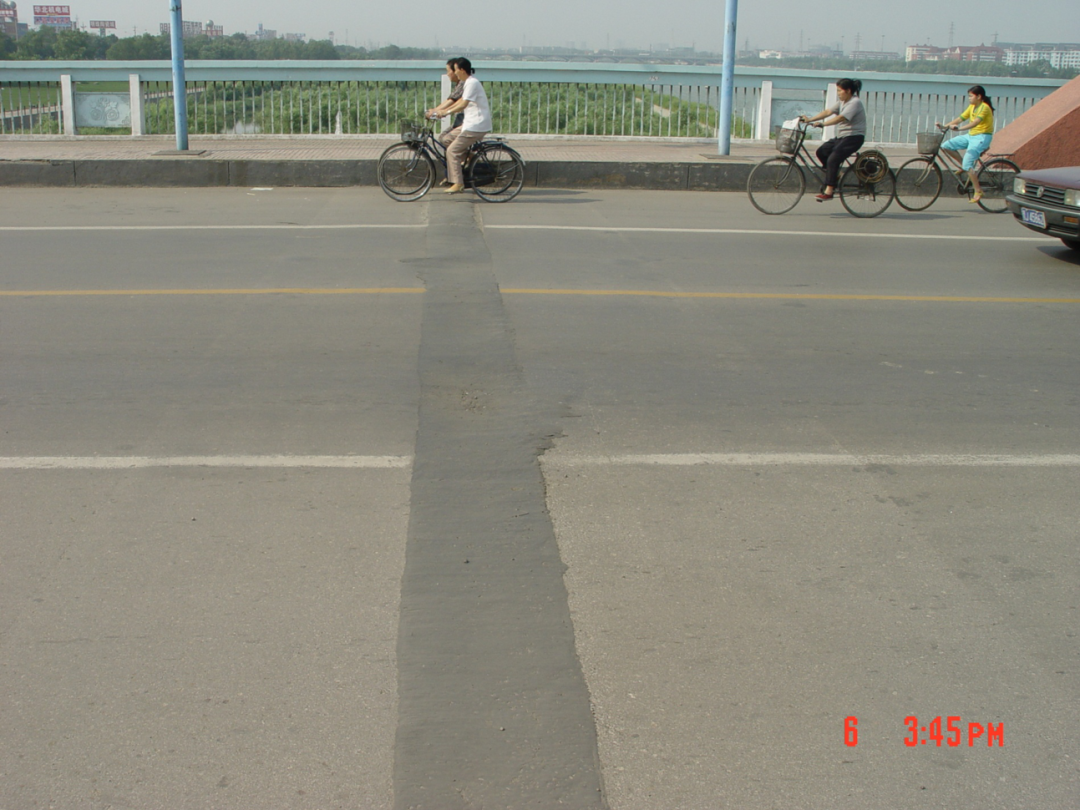
桥面连续伸缩缝
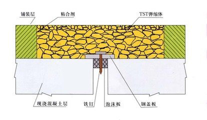

TST碎石弹性伸缩缝
TST粘合材料通常在桥面-40℃时不会变脆,夏季温度达到80℃时也不会流动。 全国范围内均可正常使用。 由于TST的高温粘合特性,施工时可牢固地粘合在现有路面上,并在常温下变得不粘,冷却后也不会被带走。 TST是一种特殊的高粘度弹塑性材料,在室温下呈弹塑性状态。 经高温熔化后,可热浇注到碎石中。 成型后,看起来像沥青混凝土。 它可以承受车辆负载并且具有弹性。 它可以代替小型混凝土。 伸缩缝功能。 施工方便快捷。 待路面冷却后即可通车。 当需要更换伸缩缝时,可半边施工。 交通繁忙路段,交通不会中断。
TST无缝伸缩缝施工技术
1)开槽:按设计要求确定槽宽,剪缝,清除清除的路面材料,清理槽口。
2)植筋:距缺口边缘5cm,向过桥方向每隔25cm打一根膨胀螺栓至缺口深度的1/2高度,并在缺口处焊一根12英寸钢筋。螺栓内螺母沿接缝方向。 。
3)填充海绵体:用高压水清洗槽口,然后用火焰加热并干燥槽口表面。 相邻梁端之间的间隙尽可能用海绵条填充,不留任何间隙。
4)将TST专用胶均匀涂抹在缺口的外露面上,等待15分钟,然后倒入融化的TST,用刮刀均匀涂抹在缺口的底部和侧面,厚度为1至2 mnl。 然后放置十字缝钢板,用定位钉固定,注意居中。
5)从槽的一端开始,放入加热后(130~150℃)的大石子。 厚度应基于可见的底层TST。 然后倒入 TST 淹没石头。 一层一层地铺开。
7)将加热后的小石块铺在桥面上方10mm处,用平板振动器振动,然后用刮刀刮平。 一般为防止下沉,应高出桥面1~2毫米。 这时可以随意修剪,用铲子平整。
8)倒入足够的TST淹没石块,防止TST流到两侧桥面。 缺口两侧可使用木板,以保持边缘整齐。
9)修整边缘,去掉两侧挡板,冷却1~2小时,即可通车。

TST碎石弹性伸缩缝
对接型
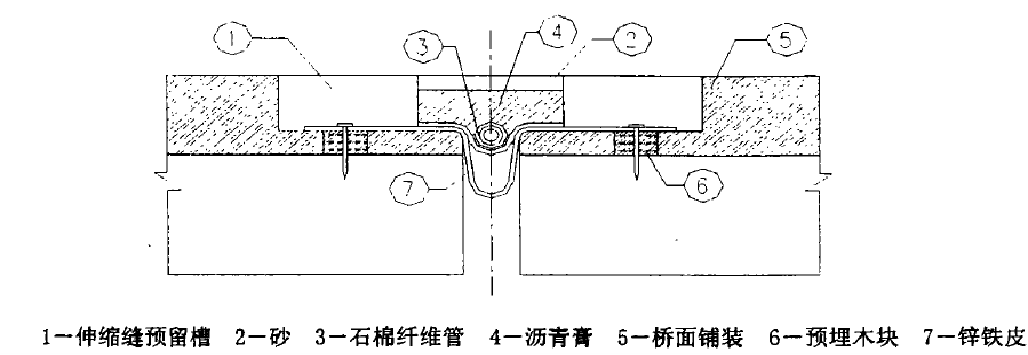
塞对接式伸缩装置是利用伸缩体的弹性来承受轮子载荷的伸缩装置。 伸缩体所用材料包括沙子、碎石以及各种形状的橡胶制品。 也有使用泡沫塑料板或合成树脂材料的。 伸缩体始终处于压缩状态。 常见的有U型锌铁片型、木板填充型、沥青填充型、矩形橡胶条、管状橡胶条型等。U型镀锌铁伸缩装置是一种填充对接式伸缩装置,广泛应用于20 世纪 70 年代和 20 世纪 80 年代。
此类伸缩装置的主要特点是:①成本低; ②所需材料易于加工; ③施工简单、容易; 这种类型一般适用于伸缩量在40mm以内的桥梁。 由于耐用性、防水性较差,使用寿命短,目前已很少使用。
嵌入式对接式伸缩装置又称异型钢式或仿毛勒式伸缩装置。 其结构原理是将不同形状的橡胶制品嵌入不同形状的钢构件中,然后通过锚固系统与接头连接。 梁体或桥台后墙整体锚固,采用异型钢为车轮提供支撑。 利用橡胶条、橡胶带的拉压和压缩来吸收梁端变形。 伸缩体可以处于压缩状态或张紧状态。 。 这是国内公路桥梁施工中广泛使用的伸缩装置。 常见的有W型、SW型、M型、PG型等。
该型伸缩装置适用于伸缩量小于80mm,即接缝宽度为20mm至80mm的桥梁结构。
此类伸缩装置的主要特点是:①结构简单、受力明确、成本低廉; ②伸缩装置主要部件由厂家加工并在施工现场安装。 与梁端的连接一般采用钢筋焊接,结构可靠,施工质量容易保证; ③耐久性好; ④防水、排水性能良好; ⑤驾驶舒适性好。
毛雷尔伸缩缝的两大设计原则是“刚性锚固”和“密封防水”
1)刚性锚杆伸缩缝锚固质量的好坏直接影响伸缩缝的使用寿命。 锚固金属板主要起传递力的作用。 经过疲劳测试的锚固装置直接焊接到侧梁上。 同时,边梁与桥梁上部结构刚性连接,保证伸缩缝承载最大的交通荷载。 在长期动态交通荷载的情况下,使用螺钉或螺栓将伸缩缝连接到桥梁上部结构的其他方法是不可行的。 毛雷尔伸缩缝在这方面的设计中率先进行了设计,将承重和防水两种功能分开并一一处理,更有利于两种功能的强化和完善。
2) 完全防水
Maurer 膨胀缝的特点之一是将氯丁橡胶密封条有效嵌入侧梁的凹槽中,确保完全防水。 同时,可以在桥面上更换或使用简单的工具进行硫化修复。 在侧梁的保护下,密封条不会被车轮直接碾压,其“V”形结构可自行清除泥沙。 密封条不仅能抵抗拉力,还能进行横向和纵向位移。 相比之下,伸缩缝漏水会对桥梁结构造成一定的破坏。
钢支撑
钢支撑伸缩装置由钢材组装而成,可直接承受车轮的载荷。 这种伸缩装置以前多用在钢桥上,现在也用在混凝土桥上。 钢支撑伸缩装置的类型、现状和尺寸较多。 主要应用广泛的是钢梳型。 钢梳式桥梁伸缩装置的结构由梳板、连接件和锚固系统组成。 有些钢梳式桥梁伸缩装置的梳齿间填充有合成橡胶,以起到防水作用。 有的还采用专门的排水沟来解决排水问题。 钢梳式桥梁伸缩装置也是钢板的指状接头。 按梳齿支撑情况分为支撑式和悬臂式。
此类伸缩装置的主要特点是:
① 所有部件均采用钢材加工组装而成,结构强度高;
② 能为车轮提供持续的支撑,提供良好的驾驶舒适性;
③与梁体连接采用预埋钢构件,连接可靠;
④ 抗冲击、振动能力强,耐久性好;
⑤能适应较大的水平位移,可用于大型桥梁。
此类伸缩装置适用于伸缩量大于40mm的桥梁,但由于成本较高,应用范围不是很广。


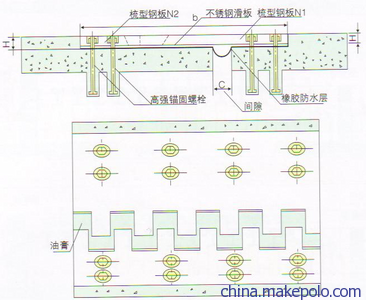
梳板式膨胀缝
橡胶板
橡胶板伸缩装置充分利用了橡胶材料的低剪切模量。 它在橡胶体内设置承重钢板和锚固钢板,并设置螺栓孔,通过螺栓与梁端连接,形成一个整体。 这种结构依靠上下凹槽之间橡胶体的剪切变形来吸收横梁的伸缩位移。 橡胶体内嵌有钢板,跨越梁端间隙,承受车轮载荷。 这种装置在我国使用较早。 全国各地有很多厂家,名称各异。 它主要在20世纪80年代和90年代使用。 本实用新型结构简单、安装方便、经济适用。 主要适用于二级以下公路桥梁,伸缩量为30mm至60mm,在我国广泛使用。
此类伸缩装置具有以下性能特点:①依靠上下钢板间橡胶体产生的剪切变形来满足结构的变形需要。 装置变形后,橡胶体内存在一定的变形能,该结构将产生一定的约束力; ② 承重十字缝钢板预埋于橡胶体内。 与钢结构伸缩装置相比,对车轮的冲击有一定的缓冲作用,有效保护伸缩装置和梁体。 、改善驾驶条件; ③伸缩装置角钢有效加强梁体端部强度。 橡胶板伸缩装置的伸缩体水平变形内力较大,一般为每延米30~35Nk左右。 变形越大,水平力越大,装置整体损坏的可能性就越大。
因此,在选择橡胶板伸缩装置时,必须考虑安装误差、温度误差等因素,选择不小于30mm的变形余量,以保证该类装置的正常使用。
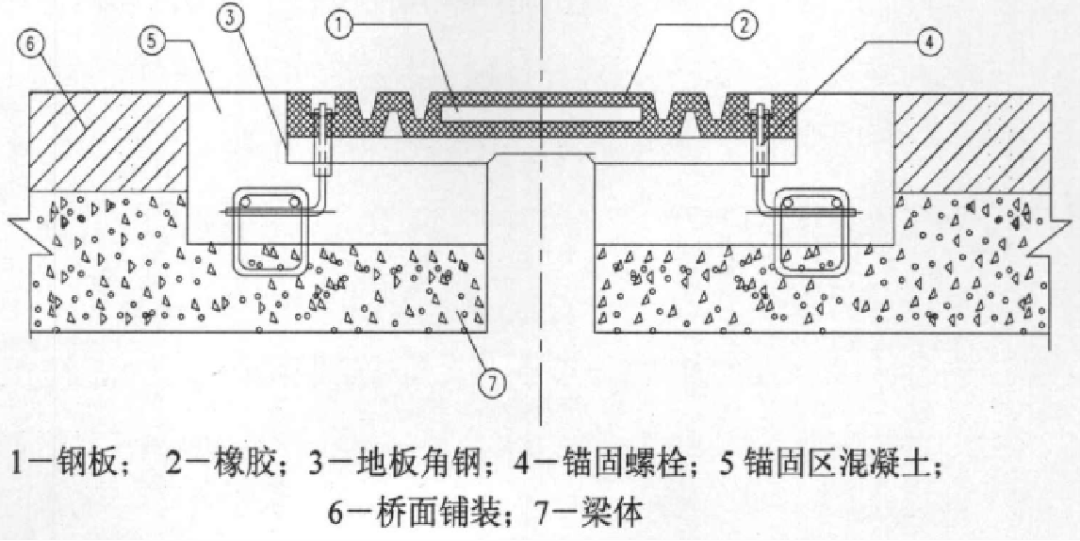

橡胶板膨胀节
模块式
组合式桥梁伸缩装置是由纵梁(异型钢)、横梁、位移控制箱、橡胶密封条等部件组成的伸缩装置。 将断面为V形或其他截面形状的橡胶密封条(带)嵌入异型钢边梁和中心梁中,形成伸缩密封体。 异型钢直接承受车轮载荷并将载荷传递到横梁上。 传递至梁体和桥台; 当伸缩装置吸收梁端变形时,位移控制箱保证异型钢之间的间隙保持均匀; 橡胶密封带可防止杂物进入且防水。 模块化伸缩装置可根据实际伸缩量增加中心梁钢和密封体的数量,可组成满足大位移的伸缩装置。 一般用于伸缩量大于80mm的桥梁。 共有15级,从8Omm单缝到12OOmm复缝。
此类伸缩装置的主要特点是:①整个伸缩装置由异型钢纵梁、钢梁、控制传动机构、位移箱、密封胶条等部件组成,结构相对复杂; ② 密封性能好,防排水性能好; ③可适用于伸缩要求较大的桥梁; ④ 整体结构刚度高,耐久性好; ⑤ 具有良好的驾驶舒适性。
但由于伸缩装置结构复杂,维护和更换需要厂家的专业技术人员。 另外,造价较高,所以一般只用于等级较高的大型桥梁。

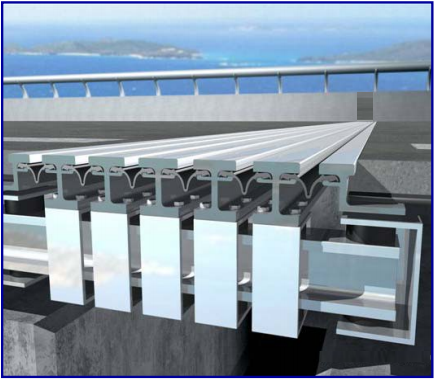
玛格巴模块化桥式伸缩装置


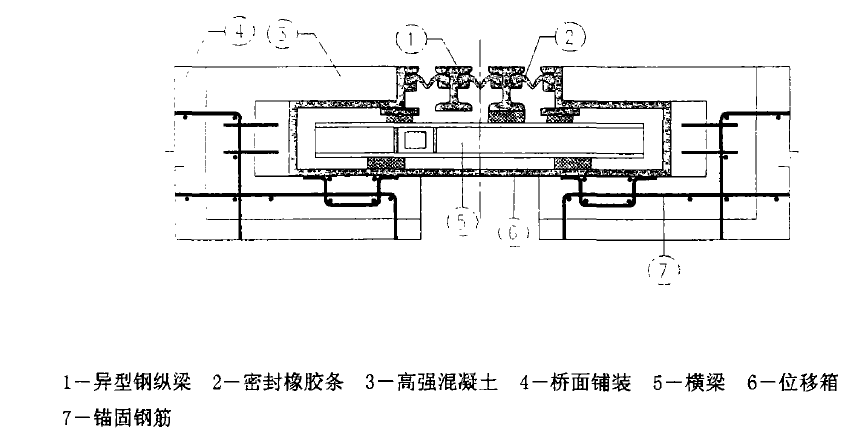
模块化桥式伸缩装置
组合式桥梁伸缩装置是由纵梁(异型钢)、横梁、位移控制箱、橡胶密封条等部件组成的伸缩装置。 将断面为V形或其他截面形状的橡胶密封条(带)嵌入异型钢边梁和中心梁中,形成伸缩密封体。 异型钢直接承受车轮载荷并将载荷传递到横梁上。 传递至梁体和桥台; 当伸缩装置吸收梁端变形时,位移控制箱保证异型钢之间的间隙保持均匀; 橡胶密封带可防止杂物进入且防水。 模块化伸缩装置可根据实际伸缩量增加中心梁钢和密封体的数量,可组成满足大位移的伸缩装置。 一般用于伸缩量大于80mm的桥梁。
此类伸缩装置的主要特点是:①整个伸缩装置由异型钢纵梁、钢梁、控制传动机构、位移箱、密封胶条等部件组成,结构相对复杂; ② 密封性能好,防排水性能好; ③可适用于伸缩要求较大的桥梁; ④ 整体结构刚度高,耐久性好; ⑤ 具有良好的驾驶舒适性。
但由于伸缩装置结构复杂,维护和更换需要厂家的专业技术人员。 另外,造价较高,所以一般只用于等级较高的大型桥梁。
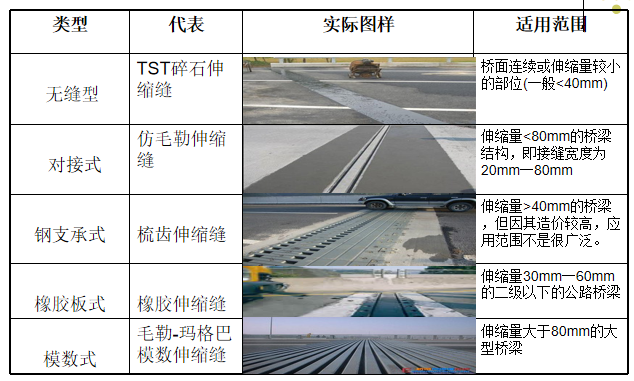
类型比较
桥梁伸缩缝设置依据
梁的伸缩量是选择伸缩缝最重要的依据
影响伸缩装置伸缩的基本因素
1、温度变化
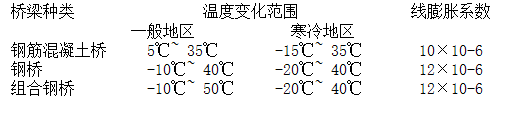
温度变化是影响桥梁伸缩的主要因素。 它分为线性温度变化和非线性温度变化。 线性温度变化对桥梁的膨胀和收缩具有主导影响。 桥梁结构处于特定的外部温度环境下,梁内温度分布不均匀,梁端部因材料热性能的变化而产生角位移。 对于小跨度(L≤8m)的桥梁,线膨胀系数很小钢结构伸缩缝设置,可以忽略不计; 对于大跨度的桥梁,设计时必须引起足够的重视。 一般设计时的线膨胀系数可按下表计算。
温度变化范围及线膨胀系数
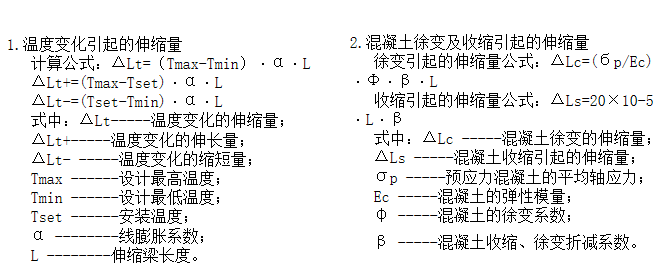
2、混凝土的收缩和徐变
混凝土的收缩和徐变是混凝土构件本身的固有特性,也是一种随机现象。 混凝土的配合比、水灰比、坍落度、水泥品种、温度、相对湿度、荷载龄期、荷载时间和强度等对混凝土的收缩和徐变影响很大。 钢筋混凝土桥梁和预应力混凝土桥梁都需要考虑其收缩和徐变。 蠕变变量的计算方法是梁在预应力作用下的弹性变形乘以蠕变系数ф=2; 收缩率按温度下降 20°C 换算。 伸缩缝安装时,收缩和蠕变已发展到一定程度。 计算时应根据安装时间减少混凝土的收缩和徐变。 其折减系数β可参照下表选取:
3、桥梁纵坡
纵坡桥梁的活动支座通常采用水平布置。 当支座发生位移时,膨胀缝不仅会产生水平位移,还会产生垂直位移(Δd),其值等于水平位移乘以纵向坡度tgθ。
4、斜桥、曲线桥的位移
斜桥或曲线桥在发生支撑位移(ΔL)方向位移时,同时也发生沿桥端线和垂直于桥端线方向的位移,即: Δd=ΔL·SINα ΔS= ΔL·COSα 式中,α——倾斜角度,ΔL——热胀冷缩量
5、各种荷载引起的桥梁应力
在活载和恒载的作用下,桥梁端部会产生角位移,使伸缩装置产生垂直、水平和角位移。 如果梁体较高,也会产生振动。
6. 地震
地震对伸缩装置位移的影响比较复杂,目前难以掌握。 设计时一般不予考虑。 但如果有可靠的数据,则可以计算出地震引起的桥墩的沉降、旋转、水平移动和倾斜量。 设计时应考虑这一点。
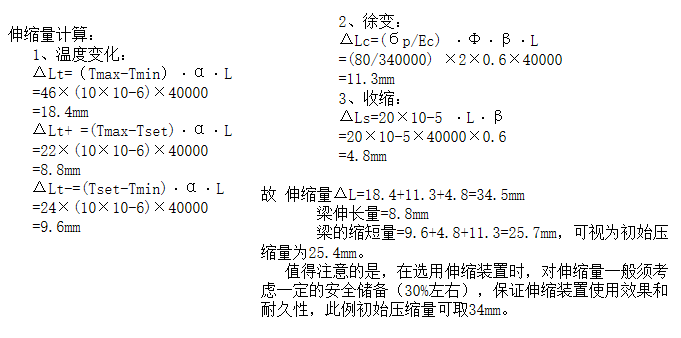
梁的伸缩计算
梁长40m的预应力混凝土梁桥; 温度变化范围-4℃~42℃; 线膨胀系数α=10×10-6; 收缩应变ε=20×10-5; 蠕变系数φ=2.0; 收缩率、蠕变折减系数β=0.6; 预应力混凝土平均轴应力σp=80kg/cm2; 混凝土弹性模量Ec=3.4×105kg/cm2; 安装温度20℃。
膨胀节的常见病害及维护
损坏形式及原因分析
在没有过载的情况下,伸缩装置的建议疲劳寿命为10至15年。
1)对于填充对接式伸缩装置,如果角钢脱落钢结构伸缩缝设置,两侧混凝土破碎,桥台一侧混凝土完全破碎,胶带断裂,坑深,维修生命可以判定已经结束。
2)对于无缝伸缩装置,如果出现明显的跳动、两侧混凝土部件断裂、严重断裂、起皱,可判断装置的使用寿命已结束。
3)对于嵌入式对接式伸缩装置,如果车辆跳动较大,桥面铺装损坏严重,则可视为其使用寿命结束。
4)对于板式橡胶伸缩装置,如果地脚螺栓脱落、橡胶老化变形、混凝土开裂,则视为其使用寿命结束。
无缝的
无缝伸缩缝的主要损坏形式有:弹性体表面明显的车辙和裂纹、弹性体表面搓板或局部剥落、局部剥落或大片骨料剥落; 或与桥面铺装接缝处桥面开裂并逐渐断裂、脱落; 或伸缩装置范围内的桥面铺装层被损坏。
损坏原因分析:弹性体填料本身材料性能存在问题,如弹性体材料吸收梁端变形的能力不足、材料强度不够、粘结材料质量不符合要求等。实际使用要求,厂家在施工时未按说明进行。 施工要求; 外界温度、荷载等因素引起的桥梁位移、旋转导致弹性体开裂、损坏; 伸缩装置结构本身的结构问题,如十字缝板强度不够等。
对接型
损坏的主要形式有:天气炎热时胶条鼓起,冬季胶条脱落,局部穿孔、渗漏; 锚固区域混凝土裂缝和碎裂; 桥面路面破损、脱落。
损坏原因分析:安装胶条时很难达到理想状态; 主锚与梁体预埋件连接薄弱,铺筑混凝土薄,后浇混凝土面层往往缺乏振动,密实度和强度较差。 某些问题导致两侧混凝土容易损坏; 锚固区混凝土与桥面铺装层连接强度不足,微裂缝发展为局部碎裂、脱落。
钢支撑
此类伸缩装置的主要损坏形式有:开焊,个别焊缝因工艺问题不易焊牢,整块钢板脱落,锚固件不牢而造成松动; 个别钢齿板已疲劳并断裂。
损坏原因分析:此类伸缩装置在加工和使用过程中容易产生变形,且难以保证齿板与垫板的贴合。 一旦出现间隙,对连接部位的受力十分不利,造成噪音、车辆跳动、昼夜作业等。 ,齿板在反复载荷作用下产生过早疲劳,紧固螺栓松动,梳板旋转外露。
橡胶板
此类伸缩装置的主要损坏形式有:橡胶板剥落,预埋钢板外露、脱落、断裂,地脚螺栓剪切、脱孔,两侧混凝土开裂、断裂,出现凹坑、沟槽等。
损坏原因分析:首先是结构本身的原因(设计原因)。 此类伸缩装置的原理是利用上下凹槽之间的橡胶剪切变形来满足梁体的伸缩。 伸缩体内嵌有钢板,承受梁端间隙的荷载。 两侧有锚钢板,通过螺栓与梁端连接。 它们每隔一米分块安装,导致完整性较差。 并且由于此类伸缩装置的水平摩擦力非常大,因此对锚固系统提出了极高的要求。 其次,产品质量不好。 例如,橡胶材料的性能、补强钢板的材质和合理布置、钢板与橡胶之间的粘结强度、生产过程中温度和湿度的控制等都非常严格。 如果有轻微的质量问题,经常会出现。 板片完全断裂、脱胶、胶层磨损、钢板外露、锚栓剪断、胶板飞出等现象,与橡胶伸缩装置的质量、横向宽度大、刚度差大有直接关系。
模块式
此类伸缩装置的主要损坏形式有:主要中心梁构件焊接,产生晃动和噪声; 热胀冷缩均匀性差; the sealing rubber belt ages, falls off or jumps out, and causes serious water leakage; cracks and grooves appear in the concrete on both sides of the device, and the bridge deck pavement The installation layer is partially broken, the anchoring system is not ideal, and local or overall damage occurs.
Analysis of the cause of damage: First of all, the side beams and center beams used in this type of domestic telescopic devices are mostly welded and connected by steel plates or shaped steel into a combined structure of special-shaped parts, and the welding quality is difficult to guarantee; and the welding strips (or clips) and screw buckles are used to tighten them When sealing rubber belts, the fasteners are prone to rust and breakage, resulting in poor structural integrity and heavy welding workload. In addition, the welding process is not up to par, making it difficult to ensure welding quality. The welding may open or the rubber belt may fall off or even jump out; secondly, installation In the reserved slot of this type of telescopic device, there are both anchor boxes and a large number of anchor steel bars, including the main steel bars in the beam body and the pre-embedded anchor steel bars, which makes pouring concrete difficult and prone to voids and denseness. Problems such as difficulty in guaranteeing and insufficient strength will cause bites, cracks, and local pits to appear during use. If not dealt with in time, serious problems such as comprehensive damage to the anchoring parts will occur.
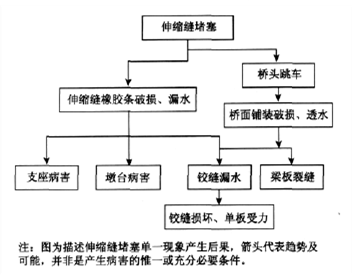
Main diseases
1. Analysis of the disease caused by too narrow expansion joints: The width of expansion joints is inappropriate during construction and installation. As a result, the reserved compression amount is insufficient, the expansion joints are squeezed, the internal stress increases, the concrete of the expansion joints is squeezed, and the road surface is damaged such as potholes.
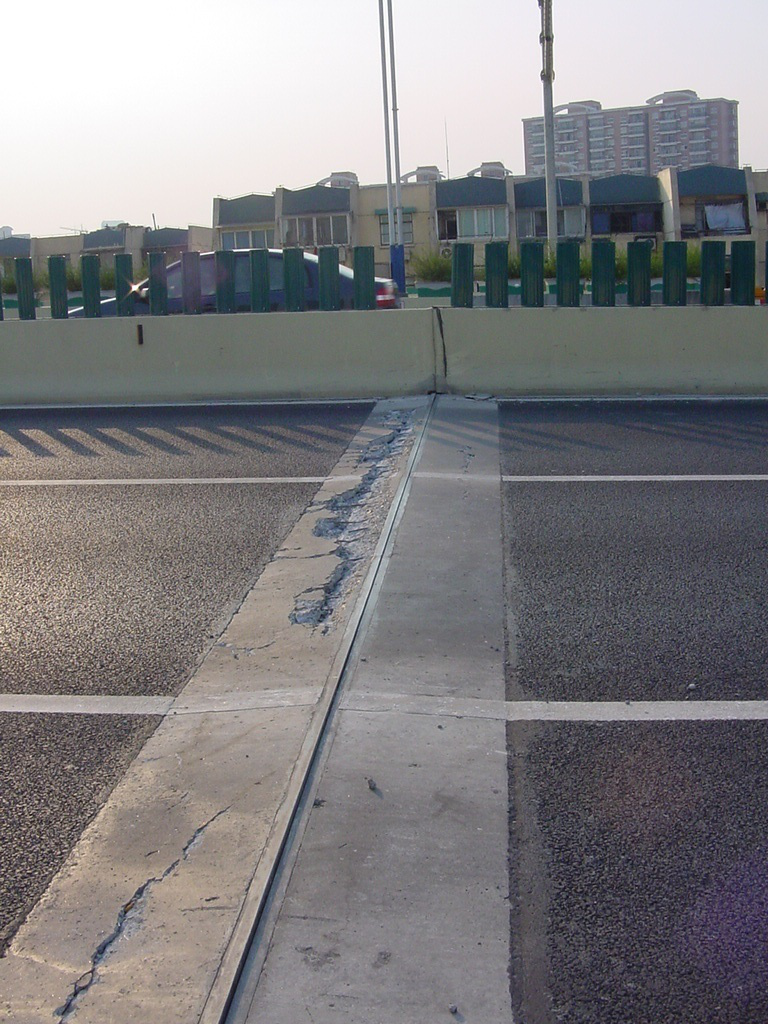

The expansion joint width has abnormal changes compared with the normal joint width reserved during design.
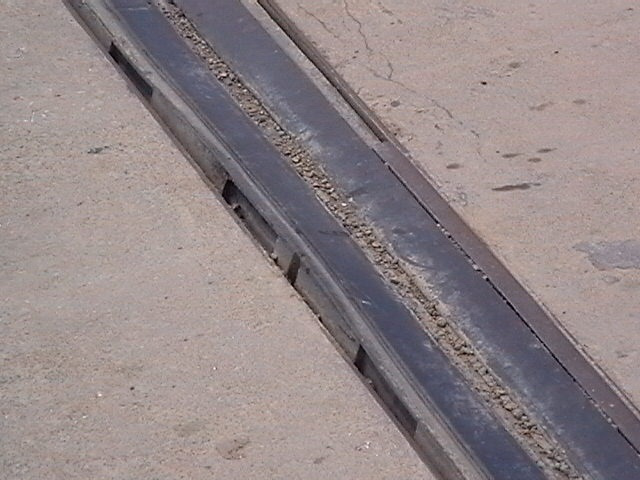
2. Expansion joint height difference disease analysis: Due to abutment subsidence, installation errors, bearing pad stone fragmentation and other reasons, one side of the bridge is lower than the road side, causing the bridge head to jump. It was inspected that the subsidence of the bridge abutment did not cause serious damage to the substructure. At the same time, the two types of diseases, bridge head jumping and expansion joint damage, are related to each other. Bridge head jumping causes a large impact load to directly act near the expansion joint, causing expansion joint damage.

3. Expansion joint blockage disease analysis: due to the accumulation of sand and other debris, expansion joints easily lose the ability to expand and contract freely. When the temperature rises in summer, the main beam cannot expand freely, and it is easy to collapse on the adjacent main beam or main beam. Thrust is generated between the beam and the abutment, and in severe cases, the main beam may be lifted or the back wall of the abutment may be cracked.
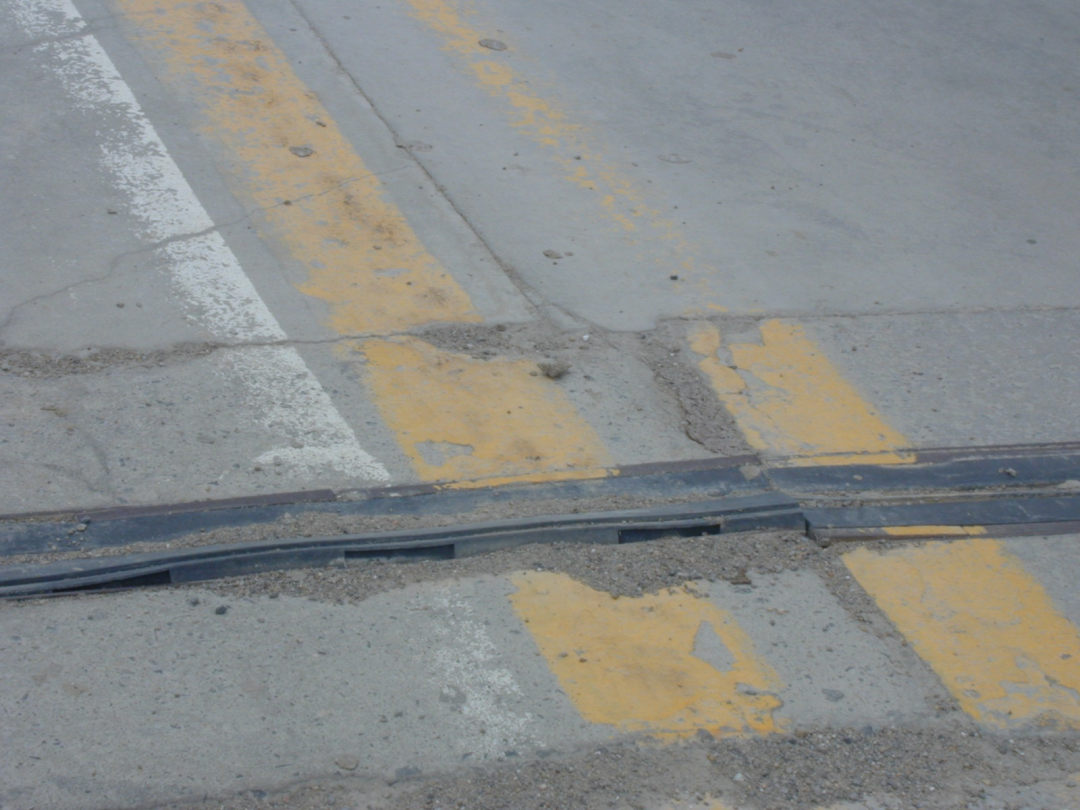


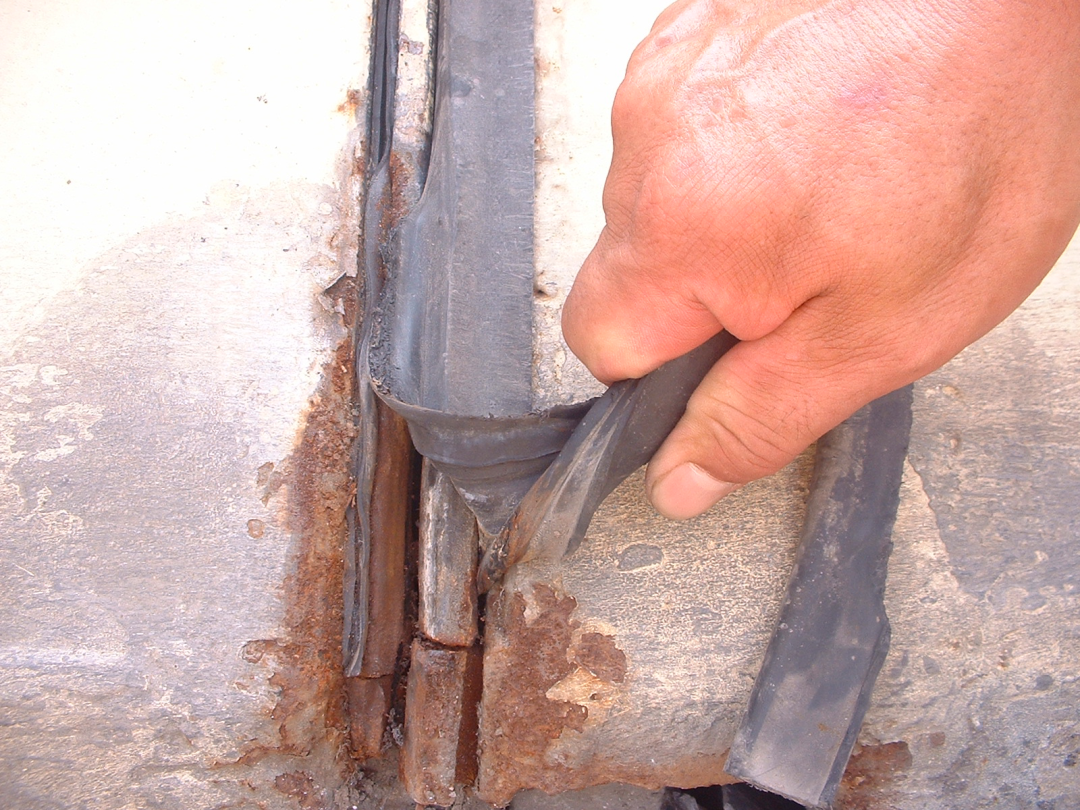
4. Analysis of damage and diseases of rubber strips in expansion joints: In addition to aging, the above three diseases of expansion joints can easily cause cracking, damage and warping of the rubber strips in the expansion joints.
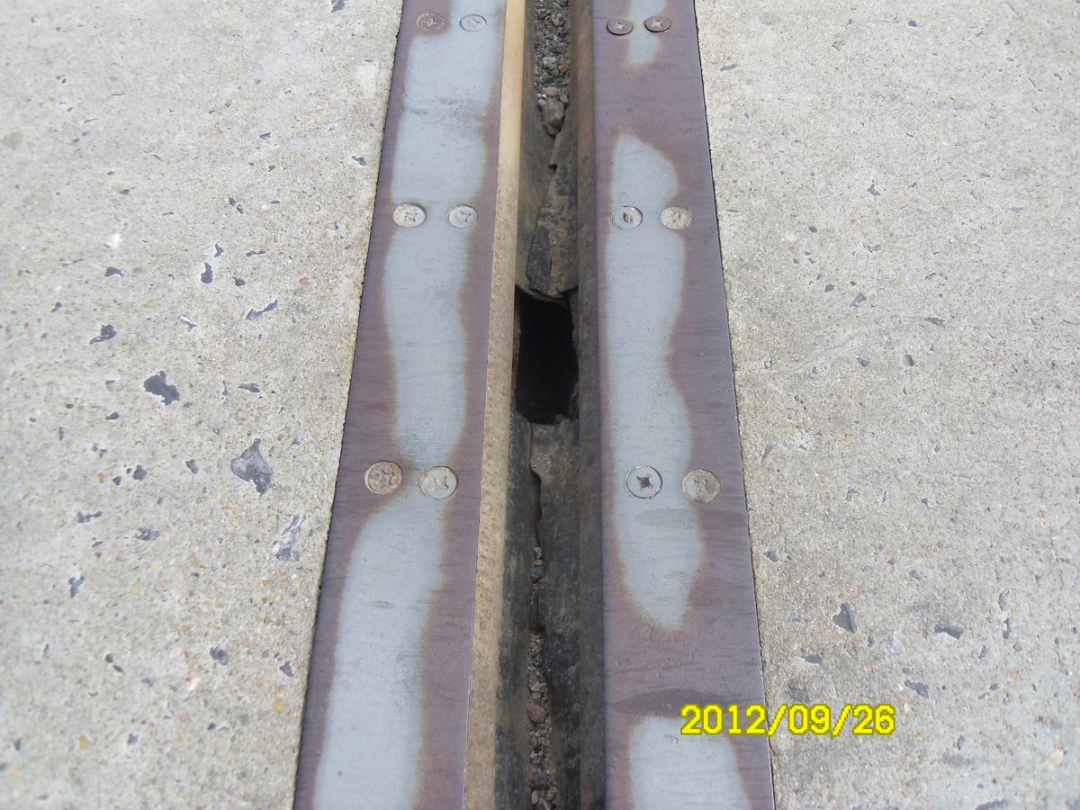


5. Analysis of damage and diseases in the anchorage area: During construction, the concrete strength of the post-poured belt in the anchorage area is insufficient, or the maintenance is not in place. Or there is a height difference with the bridge deck, causing the vehicle to jump, and the frequent action of overloaded vehicles leads to damage. It is easy to cause damage to the steel structure of the expansion joint.
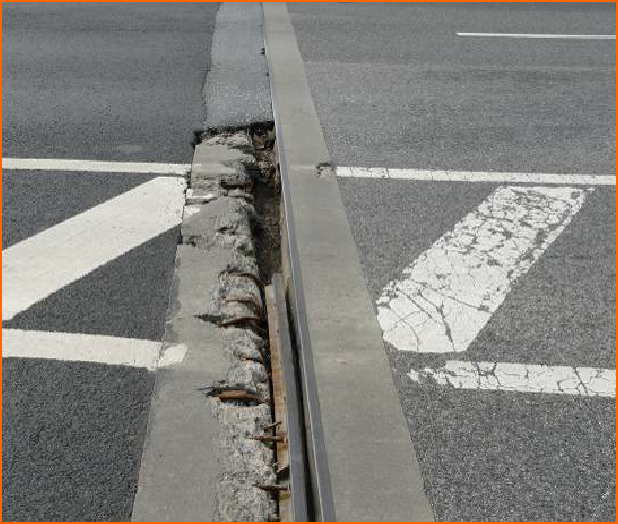


6. Water seepage in expansion joints: This is an associated disease caused by damage to the rubber strip or damage to the anchoring area. Water erosion caused by water seepage is very harmful.
Direct hazards: water seepage affects the following parts and causes corresponding hazards.
(1) The rubber of the pier (platform) bearing is aging and cracking, and the steel plate is corroded.
(2) The concrete and solid slab beams of the piers (abutments) are corroded and pitted, and the steel bars are rusted and swollen.
(3) Water accumulates in the hollow plate beam cavity
(4) Corrosion of ends of steel structure beams
Indirect hazards: Water erosion will spread to beams, plates and hinge joints, damaging upper load-bearing components. If the bridge deck pavement is permeable, the following diseases will be aggravated.
(5) The hinge seam leaks, and the hinge seam falls off seriously.
(6) Cracks in the hollow slab web.
(7) Stress on the single plate of the bridge (this disease is more serious in small and medium-sized hollow plate girder bridges).
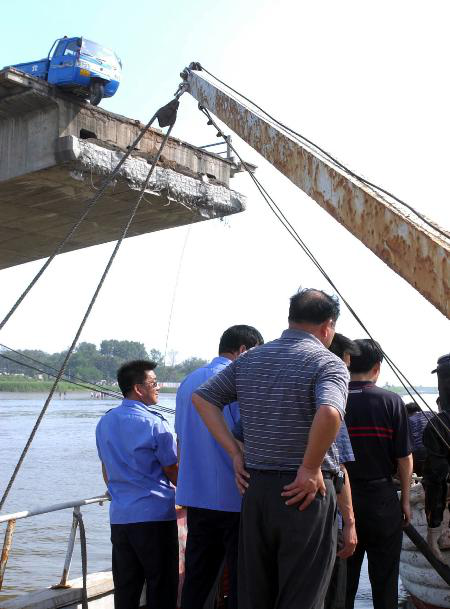
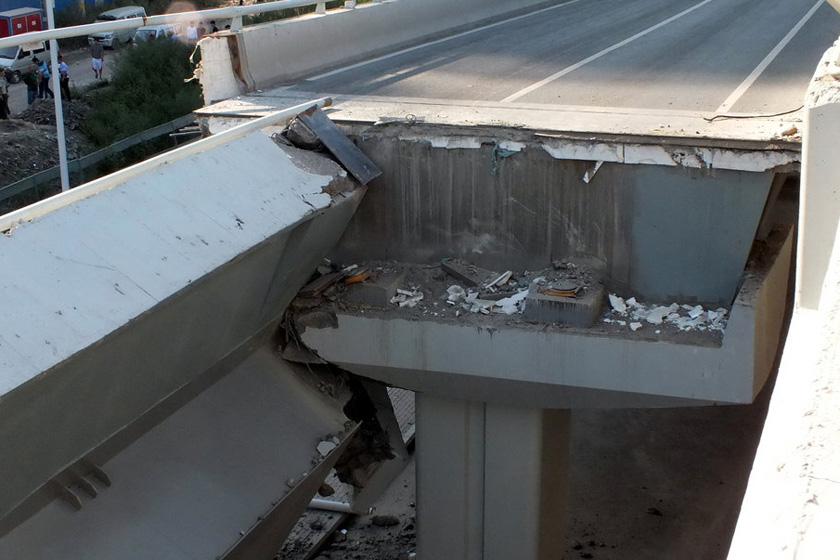
Tianzhuangtai Bridge in Panjin, Liaoning
At about 7 o'clock in the morning on June 10, 2004, the Tianzhuangtai Bridge suddenly collapsed in Panjin City, Liaoning Province. The bridge broke 27 meters in the middle. Three cars fell into the water. Two drivers and passengers of the agricultural vehicle fell into the water and escaped. Fortunately, no one died. The cause of the accident was caused by overloading.
Long-term water seepage at the expansion joints at the ends of the cantilever beams on the bridge deck caused the durability of the corbels to decrease. When heavy vehicles passed by, they suddenly broke, causing the hanging beams to fall off.

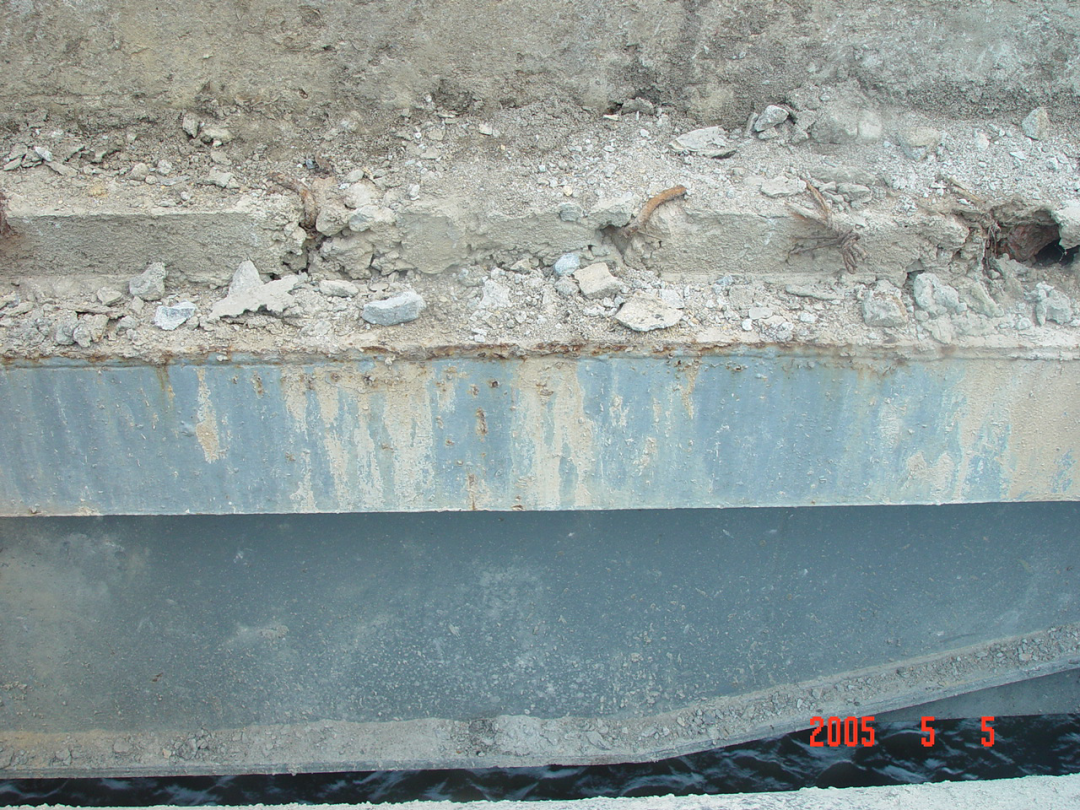
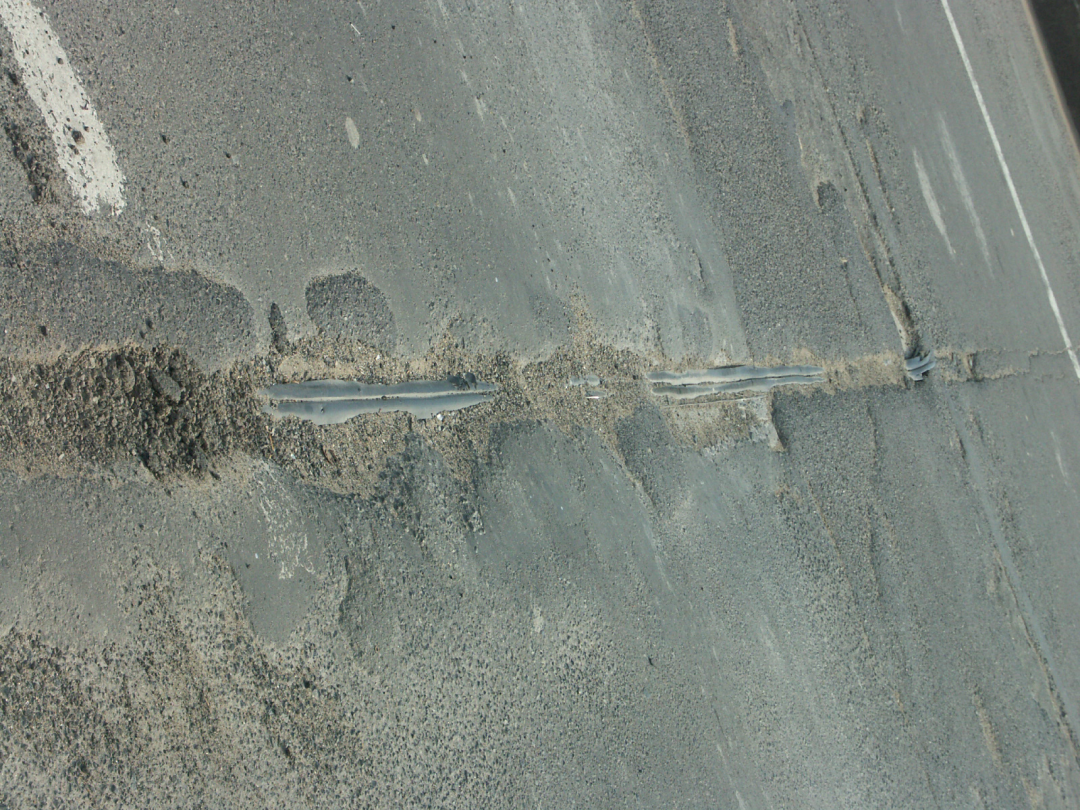
Water leakage from expansion joints

Water leakage from expansion joints
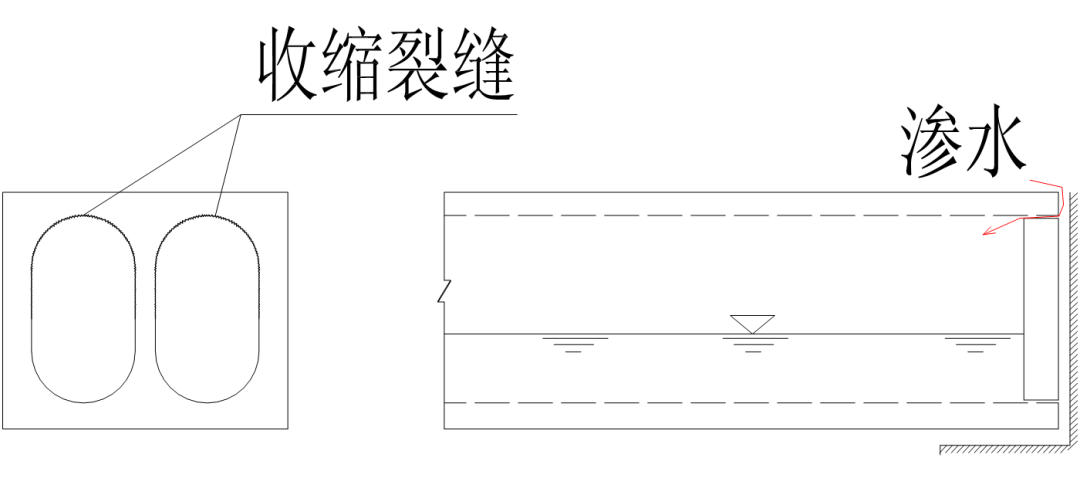
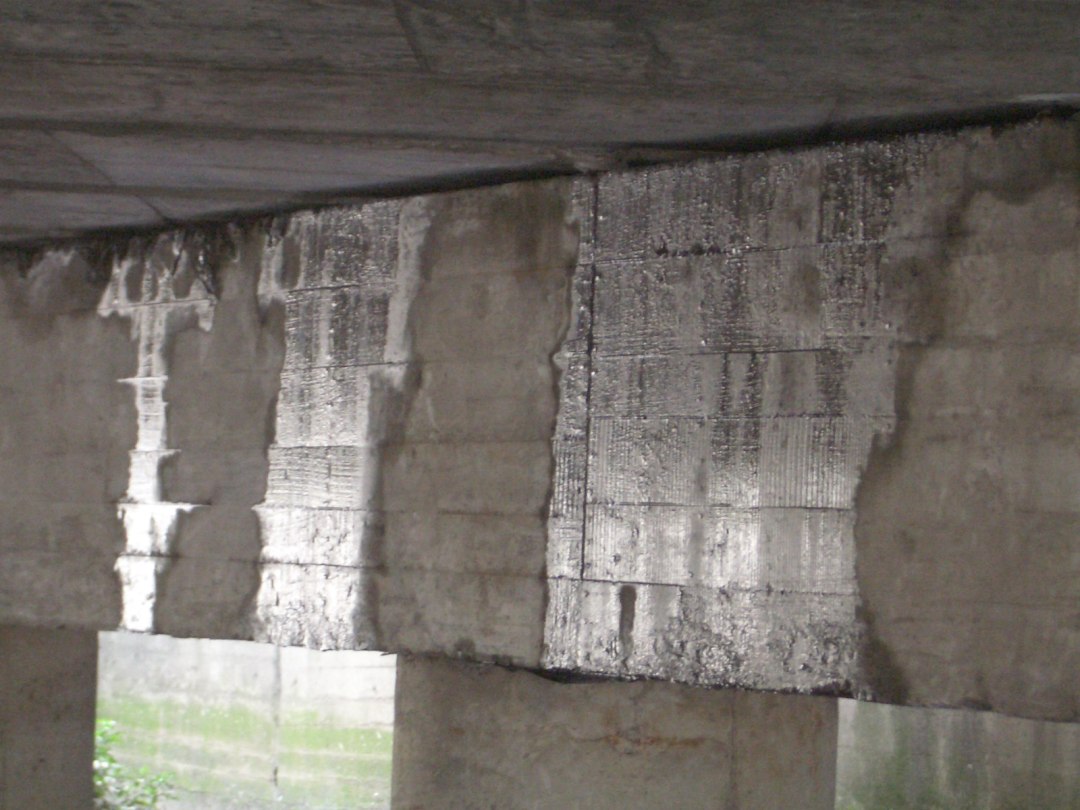
Hollow slab beam head plate mortar shrinkage cracks and water seepage
Very harmful to steel beams and hollow beams
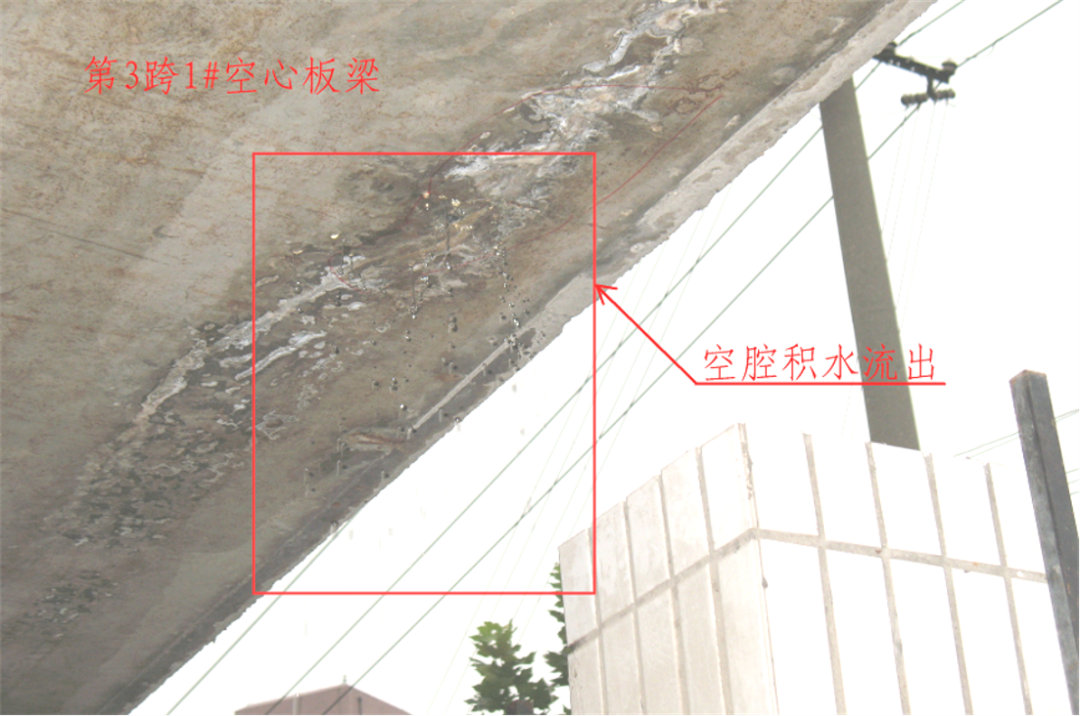
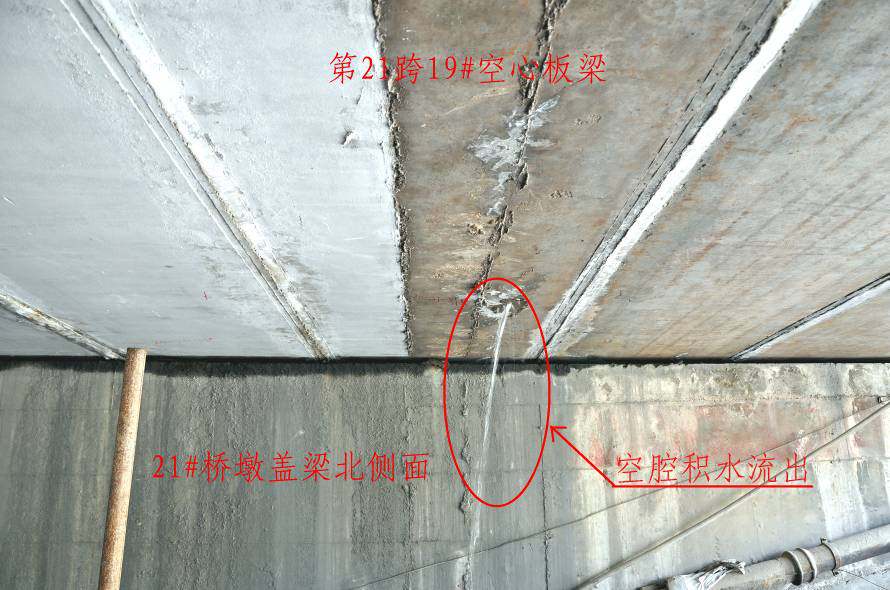


Water seeps from expansion joints and there are water marks on hollow beams. Drill holes to drain water.
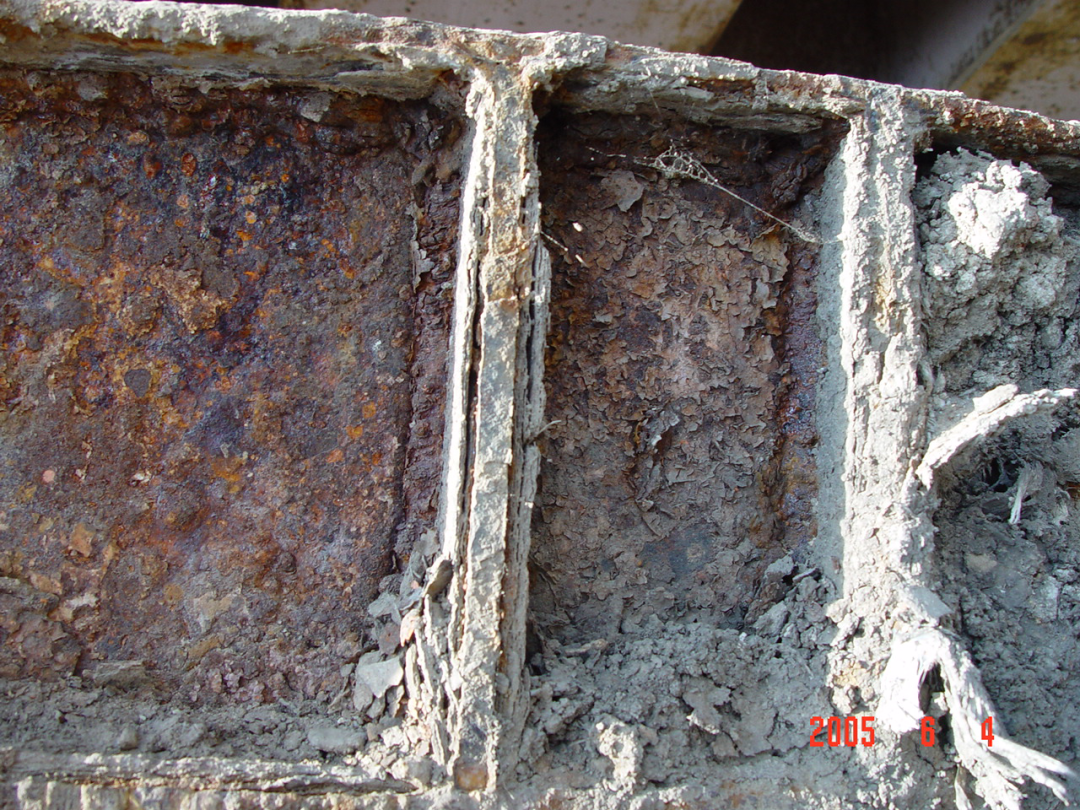
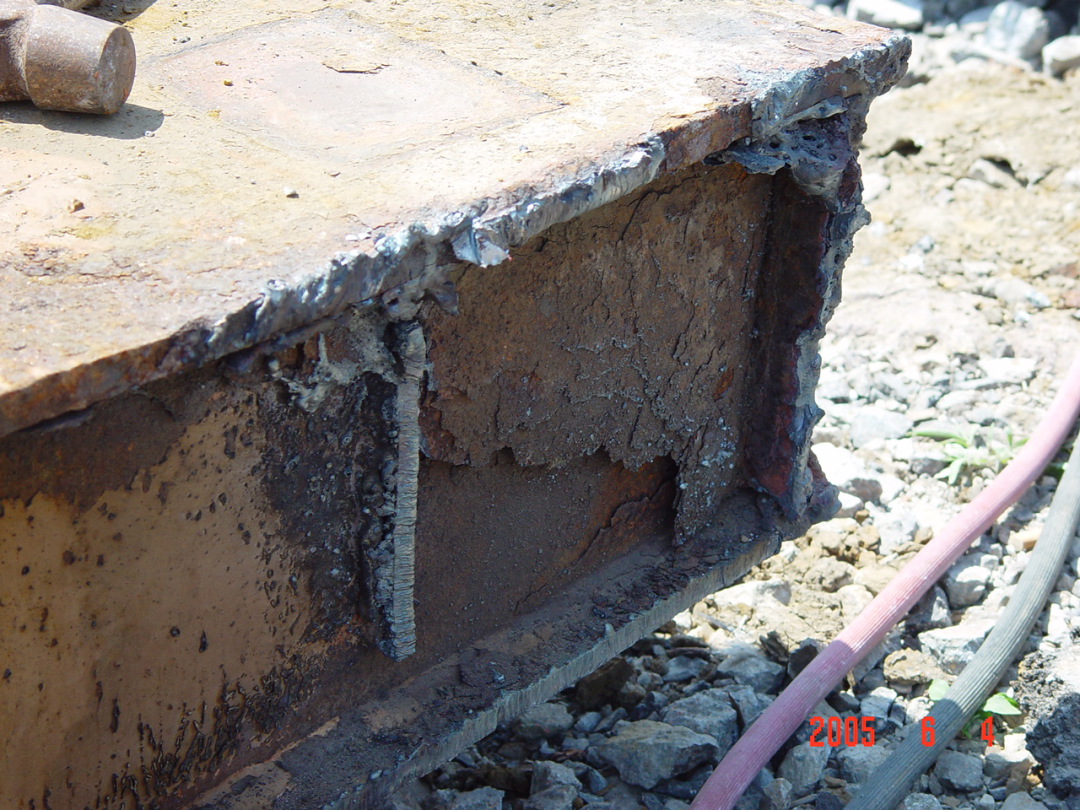



Waterproofing of expansion joints of steel structure bridges is particularly important
Main diseases
其他类型

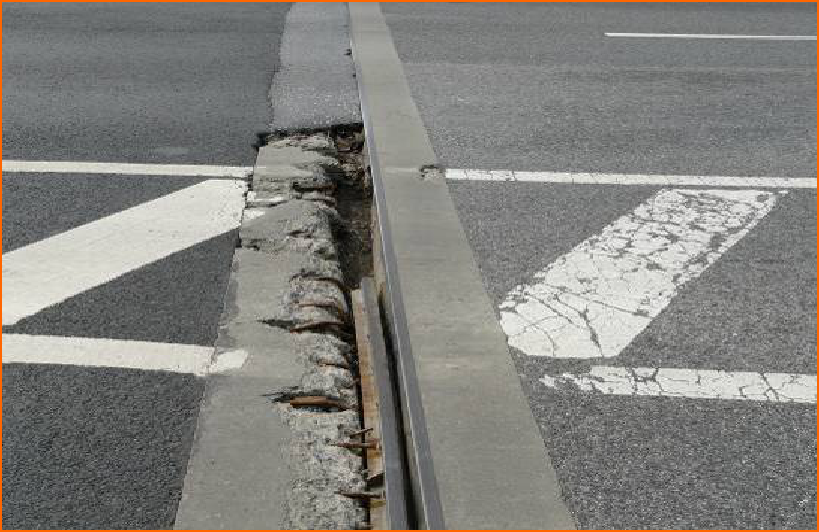
Destruction of continuous expansion joints in bridge deck

Rubber expansion joint nut loose
Expansion joint maintenance

Cross section of Harbin Mingyangtan Bridge after collapse

Completely out of control


Expansion joints are completely replaced with asphalt concrete
Clean expansion joints
Repair and replace rubber strips
Maintenance anchorage area
Integral replacement expansion joints
Expansion joint cleaning is the most important part of daily maintenance, and it is often the most overlooked.
Expansion joints are generally cleaned once a month, and the frequency needs to be increased in sections where the road surface is prone to contamination.
Do not use sharp tools when cleaning to prevent damage to the rubber strips. High-pressure water guns, high-strength fans and other equipment can be used.
Once the rubber strip is damaged, it must be repaired or replaced
Small local cracks and damage can be bonded with epoxy resin.
Those that are severely damaged or aged need to be replaced. When replacing, use a crowbar similar to changing tires to pull out the old rubber strips, and replace them with new rubber strips in the same way.

Cracks or damage in the anchorage area must be repaired immediately
Cracks in the anchorage area can be filled with epoxy resin, and epoxy mortar can be used to repair cracks with larger crack widths.
If the damage is serious, the damaged area should be chiseled out to expose the steel bars and steel parts, rust should be removed, and steel fiber concrete or rapid concrete should be poured to repair it.

Bridge expansion joint installation
工艺流程
Measure → Mark the lines → Cut the joints → Remove the concrete and debris → Install the foam board between the beams → Hoist the Maurer expansion joints into place → Adjust the plane position of the Maurer expansion joints → Adjust the elevation of the Maurer expansion joints → Anchor → Unlock → Do Good protection → pouring concrete → plastering and maintaining health → open to traffic.
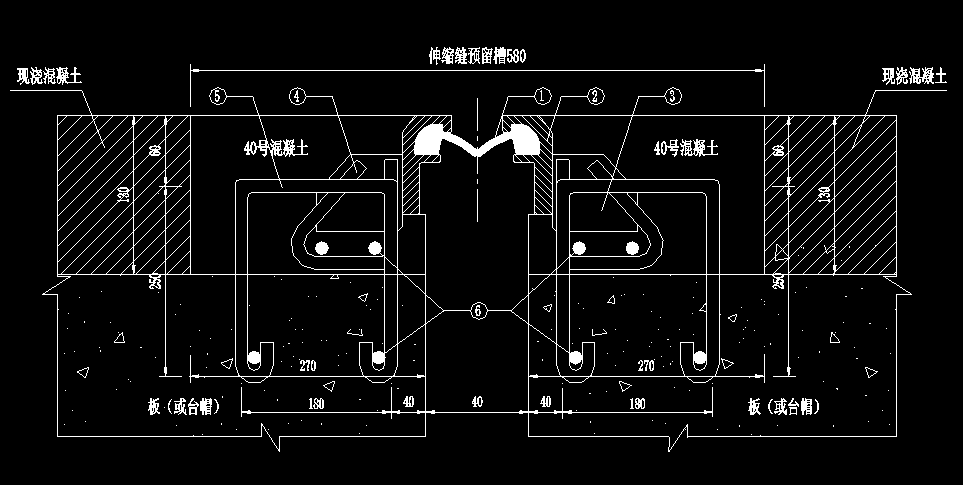
Maurer expansion joints as an example
1. Cutting and grooving: The installation of expansion joint devices should be carried out as much as possible after the road surface is paved. The size of the grooves meets the requirements for installing expansion joint devices.
2. Clean the slot: All dirt, dust and other unnecessary things must be removed.
3. Check whether the gap between the beams of the expansion joint device meets the installation temperature requirements. If it does not meet the requirements, it must be adjusted under the guidance of the engineering and technical personnel of the manufacturer to make the gap between the beams of the expansion joint device meet the design requirements. After adjustment Press the clamp again to prepare for installation
4. Taking the asphalt pavement on both sides as the elevation, place the expansion joint device in the notch, adjust the expansion joint device so that the top surface is the same as the road surface elevation, and its longitudinal and transverse slopes should be consistent with the bridge pavement.
5. Check the position of the expansion joint device, so that the position of the expansion joint device in the direction of the vertical joint and along the direction of the joint meet the design requirements. If some embedded steel bars hinder the correct direction of the expansion joint device, they can be cut off with gas cutting. 。
6. First connect and weld the anchoring steel bars on one side of the expansion joint device to the embedded steel bars in the reserved slot. During welding, you can weld one at a time, and then weld the anchoring steel bars on the other side according to the above steps. After the expansion joint device is confirmed to be fixed, the clamp can be removed, and then the remaining unwelded anchoring steel bars and the embedded steel bars are completely welded to ensure that the expansion joint device is reliably anchored.
7. If the expansion joint device is installed in sections, the joints must be welded. The welded joints of the section steel are already available in the manufacturing factory. After the two adjacent seams are aligned, they can be installed. After each beam is fully welded, it can be anchored according to the above steps.
8. Install the template on the beam end. The template should be made according to the external dimensions of the expansion joint device and the gap of the reserved slot. The template should be quite tight to prevent the mortar from flowing into the displacement control box or into the gap at the beam end.
9. After checking that the installed formwork is tight and seamless, clean the reserved groove, pour concrete (using steel fiber concrete), and vibrate and compact it. The concrete must be at least as strong as the structural concrete at that location, and the top surface of the expansion joint installation must be kept clean while the concrete is being poured.
Allowable deviation for expansion joint installation
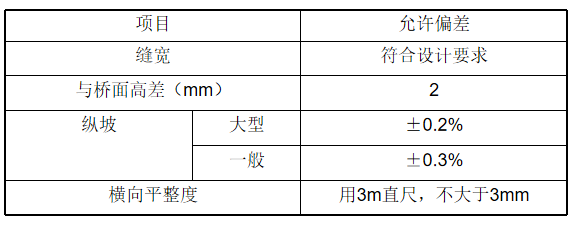
防范措施: