0 前言
2019年3月29日,住房和城乡建设部下发建科函[2019]52号《隆基二手钢结构及应急管理部关于办理交接事宜的通知》
《关于接管建设工程消防设计审查和验收职责的通知》规定,各地要完成消防救援机构对建设工程消防设计审查、消防验收、备案和抽查等工作移交住房和城乡建设部。城乡建设部门于2019年6月30日前完成。由于火灾比地震更容易发生,各地住建部门对消防更加重视,设计要求也更加严格。 除钢结构以外的建筑工程的消防设计主要由建筑、水、电、通风专业完成。 但由于钢结构工程涉及到受火构件的承载力计算,因此结构专业也涉及到。 虽然《建筑钢结构防火技术规范》GB51249-2017(以下简称《钢结构防火规范》)已经发布数年,但很多设计人员和审图人员对规范仍然不熟悉,不了解钢结构防火规范。没有严格执行。 建设工程一旦发生火灾,事故调查部门首先会审查图纸设计是否符合国家相关规定。 否则,设计、审核人员将承担相应责任。 情节严重的,设计方将承担法律责任。 随着“设计终身负责制”的广泛宣传以及地方住建部门对消防设计和验收的日益重视,越来越多的设计单位和审查机构开始关注钢结构的消防设计。项目。 但钢结构的防火规定相对复杂,全面了解并不容易。 笔者从两年前就开始关注钢结构防火设计问题。 审图时,我对未进行钢结构防火设计的图纸给出了审阅意见。 设计人员收到审查意见后,借助设计程序,基本上可以完成钢结构的防火设计。
为了给大家带来启发,笔者将自己总结的《门式刚架轻型房屋钢结构防火审查意见》提供给大家。 本审查意见针对耐火等级为二级的门式刚架灯房钢结构(以下简称门式刚性结构)。 其他钢结构工程,消防设计审查意见可在此基础上适当增减。
本文很长,第 2 部分更复杂。 大多数读者不需要阅读它。 他们只需要阅读第1、3、4、5节,然后使用设计程序(例如PKPM)即可完成消防设计; 对于那些不仅想“知其所以然”、“知其所以然”的读者,还需要阅读全文。
1、门刚性结构防火设计总体审查意见
(1)根据《建筑钢结构防火技术规范》GB51249-2017(以下简称钢结构防火规范)第3.2.1条和第3.1.2条规定,钢结构应经过防火根据结构耐火极限状态进行阻力计算和防火保护。 设计时,当经验计算的钢结构构件的耐火极限低于设计耐火极限时,应采取防火措施。
(2)提供钢结构耐火计算及防火设计计算表及《防火设计结果图》。
(3)根据《钢结构防火规范》第3.1.1条规定,柱支撑(ZC)、柱拉杆(XG)的设计耐火极限与钢柱相同。 屋顶支撑(SC)和屋顶拉杆(XG))具有与屋顶钢梁相同的设计耐火极限。 因此钢结构钢梁,除刚架钢柱、屋面钢梁的防火设计外,还应做好柱间支撑(ZC)、柱间拉杆(XG)、屋面支撑(SC)、屋面拉杆(XG)的防火设计。 )用于消防设计计算。
(4)应注意的是,根据《钢结构防火规范》第3.1.3条规定,钢结构节点的防火与防火要求最高的连接构件的防火相同。
(5)根据《钢结构防火规范》第3.1.4条及规定:
1)应标明建筑物的耐火等级:二级;
2)应注明设计耐火极限:钢柱、柱支撑(ZC)、柱拉杆(XG)为2.50小时; 屋面钢梁、屋面支撑(SC)、屋面拉杆(XG)小时1.0小时(见钢结构防火规范第3.1.1条及说明);
3)应注意钢柱、柱间支撑(ZC)、柱间拉杆(XG)采用非膨胀型防火涂料(厚型),其等效热阻Ri和等效导热系数应注明防火层。 λi与防火层厚度(即防火涂料的涂层厚度,下同)di、di不应小于15mm(见《钢结构防火涂料》第5.1.5条) 《GB14907-2018》)。
4)应注明屋面钢梁、屋面支撑(SC)、屋面拉杆(XG)是否采用膨胀型防火涂料(薄型)或非膨胀型防火涂料(厚型)。 当采用膨胀型阻燃涂料(薄型)时,只需标明阻燃保护层的等效热阻Ri,但阻燃保护层的厚度不应小于1.5mm(见“钢结构用阻燃涂料》GB14907-2018第5.1.5条); 采用非膨胀型防火涂料(厚型)时,应注明防火层的等效热阻Ri、等效导热系数λi和防火层厚度di,di不应小于15mm。
5)图中标注的Ri、λi、di响应与《消防设计结果图》及计算表一致;
(6)根据钢结构防火规范第3.1.5条应注意:当建筑所用防火材料的等效导热系数λi与设计文件要求不一致时,原则上防火层的等效热阻Ri应相等,应按规定确定防火层的应用厚度di,并经设计单位批准。 对于非膨胀型钢结构防火涂料(厚型),防火层的涂覆厚度可按钢结构防火规范附录A确定; 对于膨胀型防火涂料(薄型),厚度可直接根据涂料的等效热阻Ri确定。 应用厚度。
(7)按照《钢结构防火规范》第4.1.3.5条应注意:防火涂料与防腐涂料应兼容、配套。
(8)防火涂料应符合《钢结构用防火涂料》GB14907-2018标准。
2、审查意见逐条说明:
第(一)条审查意见:根据《建筑钢结构防火技术规范》GB51249-2017(以下简称钢结构防火规范)第3.2.1条、3.1.2条规定,钢结构结构应按照结构耐火极限状态进行耐火计算和防火设计。 当钢结构构件的耐火极限低于经验计算的设计耐火极限时,应采取防火措施。
解释如下:
1)钢结构防火设计不需进行正常使用极限状态验证,仅需进行承载力极限状态验证。 《钢结构防火规范》第3.2.1条规定:“随着温度升高,钢材的弹性模量急剧下降,构件在火灾下的变形明显大于常温应力状态。 钢结构应按正常使用极限状态进行设计。 部件防火过于严格。 因此,允许钢结构在火灾下发生较大变形,不需要进行正常使用极限状态验证。”
《钢结构防火规范》第3.2.6条规定,钢结构构件的耐火计算和防火设计可采用“耐火极限法”、“承载力法”或“临界温度法”。 这篇文章的解释指出,三者“耐火计算结果完全相同,耐火计算时只需要使用其中之一”。 PKPM程序采用“临界温度法”。
2)人工采用“临界温度法”进行钢结构耐火计算和防火设计的步骤,应按《钢结构防火规范》第7.2条的规定进行:
步骤1:根据钢结构防火规范第3.2.2条计算构件最不利荷载(作用)效应组合的设计值。
《钢结构防火规范》第3.2.2条计算的构件最不利荷载(作用)效应组合依据国家标准《建筑可靠性统一设计标准》GB50068-2001和《建筑结构荷载规范》 GB50009-2012对偶然设计工况制定了荷载(作用)效应组合原则,取恒荷载、地板或屋顶活荷载和风荷载作为火灾发生时最可能的值。 此外,还应考虑根据火灾结构温度标准值计算的荷载效应值。 至于地震的影响,则无需考虑,因为地震后,建筑物内经常会发生火灾等次生灾害,但火灾期间发生较大地震的概率极小。 (参见《钢结构防火规范》第3.2.2条的说明)
步骤2:根据构件和荷载类型,按《钢结构防火规范》第7.2.1条至第7.2.7条计算构件的临界温度Td。
临界温度Td是指钢构件受火达到其耐火承载力极限状态时的温度。 根据截面强度荷载比R或R'查表7.2.1~表7.2.5可得。 负载比R或R'越大(相当于元件截面越小),临界温度Td越小。 由于表7.2.1~表7.2.5中R或R'≤0.9,当R或R'>0.9时,防火设计将无法进行。 也就是说,当构件截面较小时,可以不考虑防火设计。 承载力勉强够用,但防火设计时防火层厚度过大,甚至无法进行防火设计。 在这种情况下,应增加组件部分。 (截面强度荷载比R或R'相当于不考虑防火计算时的应力比)
步骤3:根据钢结构防火规范第6.2.1条计算设计耐火极限tm内不带防火构件的最高温度Tm。
按钢结构防火规范第6.2.1条计算达到耐火极限时的TS为Tm。 本文的描述指出,公式(6.2.1-1)是增量公式,需要逐步迭代计算。 手动计算非常麻烦。 《钢结构防火规范》第6.2.1条的解释“表10”给出了按式(6.2.1-1)计算的无防火钢构件的温度Tm,可根据交叉式计算无防火钢构件的截面形状系数F。 可求出/V(单位为m-1)和耐火极限tm。 截面形状系数F/V是指钢构件着火表面积与其相应体积之比,按钢结构第6.2.1条解释的公式“表9”计算消防规范。
步骤4:当Td>Tm时,构件的耐火性能满足要求,无需进行防火处理; 当Td≤Tm时钢结构钢梁,构件的耐火性能不符合要求,应进行防火处理。 根据下面的第五步和第六步确定组件。 所需的防火措施。
大多数情况下,Td≤Tm需要防火。 如下例(步骤 6)所示,Td=621.49。 C、“无保护钢构件最高温升(Ts)”为Tm,Tm=Ts=1081.71。 C、Td≤Tm,应进行防火处理。
只有在极少数情况下(负载率低、截面形状系数小、耐火极限小)才会出现Td>Tm,不需要防火。 例如,轴拉构件,荷载比R=0.3,截面为圆形,直径d=0.25m,耐火极限为1.0小时。 临界温度Td=663查钢结构防火规范第7.2.1条“表7.2.1”。 C; 根据钢结构防火规范第6.2.1条“表9”,截面形状系数F/V=4/d=4/0.25=16(m-1),查第6.2.1节钢结构防火规范的规定 按“表10”(线性插值法)的规定,不带防火保护的钢构件温度为Tm=627。 C、Td>Tm,若构件的耐火性能满足要求,则无需防火。 但事实上,负载比R=0.3的情况很少出现,因为截面太大,造成浪费。
第五步:确定防火方式(门刚性结构一般采用喷涂防火材料防护),计算防火防护钢构件的截面形状系数Fi/V(单位:m-1) 。
防火钢构件截面形状系数Fi/V(单位:m-1)的计算方法见《钢结构防火规范》第6.2.2条第2款。 对于外缘防火(如喷涂防火涂料保护),防火钢构件的截面形状系数Fi/V等于未防火钢构件的截面形状系数F/V。
第六步:按《钢结构防火规范》第7.2.8条、第7.2.9条确定防火厚度。
例如:某工程钢柱1参数如下:


截面形状系数Fi/V=225(1/m),临界温度Td=621。 C、耐火极限(耐火时间)tm=2.50小时=2.5x60x60=9000s,按钢结构防火规范(7.2.8-1)第7.2.8条规定,防火层的等效热阻Ri=5x10-5x(Fi/V)/{(Td-Ts0)/tm+0.2]2-0.044}=5x10-5x225/{(621-20)/9000+0.2]2-0.044}=0.414m2* oC/W,与程序计算结果0.4345 m2*oC/W基本一致。本例采用非膨胀型防火涂料(厚型),等效传热系数
λi输入为0.05W/(m*oC),防火层厚度按钢结构防火规范第7.2.8条(7.2.8-2)规定。
di=Riλi=0.414x0.05=0.207(m)=20.7(mm),与程序计算结果21.72mm基本一致。
(二)审查意见:提供钢结构耐火计算及消防设计计算表及《消防设计结果图》。
说明:程序进行耐火计算和消防设计后,生成“消防设计结果图”,如下图:
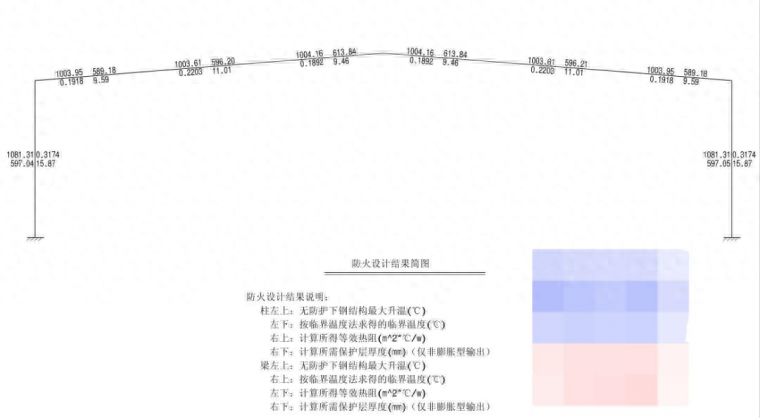
设计提供“防火设计结果简图”后,审图人员可以检查图中标明的防火层的等效热阻Ri和厚度di是否正确(本例中为等效传热系数 λi 为 0.05W/(m*oC) 输入)。
审查意见(3):根据《钢结构防火规范》第3.1.1条规定,柱支撑(ZC)、柱拉杆(XG)的设计耐火极限与钢柱相同。 屋顶支撑(SC)和屋顶盖拉杆(XG)的设计耐火极限与屋顶钢梁的设计耐火极限相同。 因此,除刚架钢柱、钢梁的防火设计外,还对柱间支撑(ZC)、柱间拉杆(XG)、屋面支撑(SC)和屋顶拉杆 (XG)。
解释:
1)一般柱支撑用符号ZC表示,屋面支撑用符号SC表示,柱拉杆和屋面拉杆均用符号XG表示。
当使用其他符号时,应作相应修改。
2) 柱支撑(ZC)和柱拉杆(XG)、屋顶支撑(SC)和屋顶拉杆(XG)可手动设计防火,或
提供消防设计程序。 使用PKPM程序进行设计时,可以在“工具箱”中进行计算。 笔者在审图过程中发现,不少设计并未对柱支撑(ZC)、柱拉杆(XG)、屋面支撑(SC)、屋面拉杆(XG)进行单独的防火设计,而是采用柱支撑。 支撑(ZC)、柱间拉杆(XG)的防火与钢柱相同,屋顶支撑(SC)、屋面拉杆(XG)的防火与钢梁相同。 当风荷载较小,门刚体结构高度和跨度较小,柱间支撑(ZC)数量较多时,这种做法比较安全; 当风荷载较大,门刚体结构高度和跨度较大,柱间支撑(ZC)数量较多时,数量较少时,这种做法可能不安全。
(四)审查意见:应注意的是,根据《钢结构防火规范》第3.1.3条规定,钢结构节点的防火与防火要求最高的连接构件的防火相同。
说明:钢结构的节点也应采取防火措施,并应与连接构件中防火要求最高的节点相同。
第(五)条审查意见:根据第3.1.4条和《钢结构防火规范》的规定:
1)应标明建筑物的耐火等级:二级;
2)应注明设计耐火极限:钢柱、柱间支撑(ZC)、柱间拉杆(XG)为2.50小时; 屋顶钢梁、屋顶支撑
支撑(SC)和拉杆(XG)均为1.0小时(见钢结构防火规范第3.1.1条及说明)。
3)应注意钢柱、柱间支撑(ZC)、柱间拉杆(XG)采用非膨胀型防火涂料(厚型),防火
防护层的等效热阻Ri、等效导热系数λi和防火层厚度(即防火涂料的涂层厚度,下同)di,di不应小于15mm(参见《钢结构用防火涂料》GB14907-2018第5.1.5条)。
4)应注明屋面钢梁、屋面支撑(SC)、屋面拉杆(XG)是否采用膨胀型防火涂料(薄型)或非膨胀型防火涂料(厚型)。 当采用膨胀型阻燃涂料(薄型)时,只需标明阻燃保护层的等效热阻Ri,但阻燃保护层的厚度不应小于1.5mm(见“钢结构用阻燃涂料》GB14907-2018第5.1.5条); 采用非膨胀型防火涂料(厚型)时,应注明防火层的等效热阻Ri、等效导热系数λi和防火层厚度di,di不应小于15mm。
5)图中标注的Ri、λi、di响应与《消防设计结果图》及计算表一致。
解释:
1)本说明适用于耐火等级为二级的建筑物。 当为其他级别时,应作相应修改。
2)本说明是对不带夹层的门刚性结构的说明。 当存在夹层时,还应标明夹层楼板梁和楼板支撑的耐火等级。
3)《钢结构防火规范》第4.1.3条第2款规定:“设计耐火极限大于1.50小时的构件不应采用膨胀型防火涂料。” 由于钢柱、柱间支撑(ZC)和柱间拉杆(XG)的耐火极限分别为3.00小时(一级)、2.50小时(二级)、2.00小时(三级)。 因此,根据本文规定,耐火等级为一级、二级、三级(ZC)的钢柱、柱间支撑和柱间拉杆(XG)宜采用非膨胀型防火涂料(厚型) ,不宜使用膨胀型防火涂料(薄型)。 对于非膨胀型防火涂料(厚型)的最小厚度,钢结构防火规范与《钢结构防火涂料》GB14907-2018有所不同:前者第4.1.3条第4款规定:“非膨胀型防火涂料厚度不应小于10mm。” 后者第5.1.5条规定:“非膨胀型钢结构防火涂料的厚度不应小于15毫米。” 因此,严格要求非膨胀型防火涂料保护层厚度di不应小于15mm。
4)屋面钢梁、屋面支撑(SC)、屋面拉杆(XG)设计耐火极限分别为1.5小时(一级)、1.0小时(二级)、
0.5 小时(3 级)和不需要(4 级)不超过 1.5 小时。 因此,膨胀型防火涂料(薄型)可用于屋顶钢梁、屋顶支撑(SC)和屋顶拉杆(XG)。 也可采用非膨胀型防火涂料(厚型)。
当采用膨胀型阻燃涂料(薄型)时,只需在图中注明阻燃保护层的等效热阻Ri。 其厚度在施工时根据具体的防火涂料按以下方法确定:防火涂料供应商应提供最大使用厚度、最小使用厚度的等效热阻Ri、等效热阻Ri以最大使用厚度与最小使用厚度之差的1/4为增量确定阻燃涂层的厚度Ri,然后采用线性插值法确定阻燃层厚度di(见钢结构防火规范第7.2.8条的说明)。 例如某膨胀型防火涂料供应商提供的参数如下:当厚度di为2.0mm(最小厚度)时,对应的等效热阻Ri为0.10m2*oC/W,当厚度di为3.0mm,对应的等效热阻Ri为0.10m2*oC/W。 热阻 Ri 为 0.15 m2*oC/W。 当厚度di为4.0mm时,对应的等效热阻Ri为0.20m2*oC/W。 当厚度di为5.0mm时,对应的等效热阻Ri为0.25m2*oC。 /W,当厚度di为6.0mm(最大厚度)时,对应的等效热阻Ri为0.30 m2*oC/W。 若某工程屋面钢梁采用该膨胀型防火涂料,则所需防火层的计算等效热阻Ri不应小于0.25m2*oC/W,厚度di不应小于5.0毫米。
当采用非膨胀型防火涂料(厚型)时,应注明防火层的等效热阻Ri、等效导热系数λi和防火层厚度di。 它们之间的关系为:di=Riλi。 (参见钢结构防火规范第7.2.8条第2款)
5)《防火设计结果图》及计算书包括各构件防火层的等效热阻Ri。 当为非膨胀型防火涂料(厚型)时,还给出防火层的厚度di,应取钢梁(钢柱)所有构件中的最大等效热阻Ri和di并在图中标出它们。 图中标注的非膨胀防火涂料(厚型)的等效导热系数λi也应与计算书上录入的一致。
(六)审查意见:按照《钢结构防火规范》第3.1.5条的规定,应注意:当施工中使用的防火材料的等效导热系数λi与设计文件的要求不一致时,应采用防火层的等效导热系数。 保护层的应用厚度按等阻原则确定,并应经设计单位批准。 对于非膨胀型钢结构防火涂料(厚型),防火层的涂覆厚度可按《建筑钢结构防火技术规范》GB51249-2017附录A确定; 对于膨胀型防火涂料(薄型),可根据涂层的厚度确定防火层的厚度。 有效热阻直接决定其应用厚度。
说明:使用PKPM程序进行防火计算时,非膨胀防火材料(厚型)的等效导热系数λi默认为0.10 W/(m*oC),可以修改。 当建筑所用防火材料的等效导热系数λi与图示不一致时,应根据防火层的等效热阻Ri为原则确定防护层的应用厚度。等于,即按照《钢结构防火规范附录A》计算,采用公式(A-1):di2=di1λi2/λi1。 其中:di2为建筑所用防火层的厚度; di1为图中标注的防火层厚度; λi2为建筑用非膨胀型防火涂料(厚型)的等效导热系数; 图中λi1为防火层厚度非膨胀型防火涂料(厚型)所示的当量导热系数。
第(七)条审查意见:应按照《钢结构防火规范》第4.1.3.5条规定:防火涂料与防腐涂料应兼容、配套。
说明:《钢结构防火规范》第4.1.3.5条规定:“应特别注意防火涂料与防腐涂料的相容性,特别是膨胀型防火涂料,因为它们与防腐涂料一样都是有机材料。并可能引起化学反应。 反应。 无法出具第三方证明材料证明防火材料与防腐涂料相容性的,应当委托第三方进行测试验证。 膨胀型防火涂料和防腐涂料的施工顺序为:防腐底漆、防腐中间漆、防火漆。对于涂料和防腐面漆,防腐底漆和中间漆的厚度应be controlled during construction to avoid the shedding of the fire-retardant coating due to high temperature degeneration of the anti-corrosion primer and intermediate paint, and to avoid affecting the expansion type due to the top paint being too thick or too hard. Foaming expansion of fire retardant coatings.”
Article (8) Review opinion: Fire retardant coatings should meet the "Fire retardant coatings for steel structures" GB14907-2018 standard.
Explanation: There are many fire-retardant coatings on the market, so it should be clear that fire-retardant coatings should meet the "Fire-retardant Coatings for Steel Structures" GB14907-2018 standard.
3. Questions about parameters
(1) The physical parameters of steel at high temperatures include thermal expansion coefficient αs, heat transfer coefficient λs, specific heat capacity cs and density ρs. The values are determined according to "Table 5.1.1" in Article 5.1.1 of the Steel Structure Fire Protection Code. The PKPM program also determines the values accordingly. ,Can not be modified;
(2) Physical parameters of fire protection materials:
1) Specific heat capacity ci of fire protection materials: The steel structure fire protection code does not specify a value, and the PKPM program defaults to 1000J/(kg*oC). The author found from relevant information that when the temperature changes from 20 to 1000 oC, ci changes from 1187 to 1676J/(kg*oC). The default setting of PKPM program is 1000J/(kg*oC) which is on the safe side.
2) Density ρi of fire protection materials: The steel structure fire protection code does not specify a value, and the PKPM program defaults to 680kg/m3. Articles 5.2.1 and 5.2.2 of "Steel Structure Fire Retardant Coatings" GB14907-2018 stipulate that the dry density shall not be greater than 500 kg/m3 (indoor) and 650 (outdoor) kg/m3.
3) For fire-retardant coatings, since it is a lightweight fire-retardant protective layer (see the description of Article 6.2.2 of the Steel Structure Fire Protection Code), it should be used according to Article 6.2.2 of the Steel Structure Fire Protection Code, Style 2 (6.2.2-3), In formula (6.2.2-4), α has nothing to do with the specific heat capacity ci and density ρi of the fire protection material, so the values of ci and ρi do not affect the results.
4. Fire protection design issues of round steel supports
In door rigid structures, round steel column supports (ZC) and round steel roof supports (SC) are widely used. For column supports (ZC), Article 8.2.3 of the "Technical Specifications for Steel Structures of Portal Rigid Frame Lightweight Houses" GB51022-2015 stipulates that except when there is a crane, the steel column cross supports must be used below the corbels, in all other cases Round steel column supports (ZC) can be used; for roof supports (SC), Article 8.3.2 of the "Technical Specifications for Steel Structures of Portal Rigid Frame Lightweight Houses" GB51022-2015 stipulates that except when the roof diagonal beams bear the load of a suspended crane Except for the cross bracing between shaped steel columns, which must be used for the lateral support of the roof, round steel roof supports (SC) can be used in other cases. Therefore, the fire protection design of round steel supports (ZC and SC) is very important.
Since the diameter of round steel supports (ZC and SC) is generally not greater than 25mm, if non-expandive fire retardant coating (thick type) is used, the thickness is at least 15mm, and the construction is too difficult. Even if the construction is reluctant, due to its small stiffness, vibration and deformation are prone to occur. Thick fire retardant coatings will peel off. Therefore, the roof round steel support (SC) should use intumescent fire retardant coating (thin type) as much as possible. At the same time, the design fire resistance limit of the roof support (SC) is 1.5 hours (level 1) and 1.0 hours (level 2), both of which are not large. 1.5 hours, it can also meet the requirements of Article 4.1.3, Paragraph 2 of the Steel Structure Fire Protection Code, "Components with a design fire resistance limit greater than 1.50 hours should not use intumescent fire retardant coatings."
For the round steel supports between columns (ZC), the author recommends the inter-column supports of portal frames with a fire resistance level of level 3 (fire resistance limit is 2.0 hours) and the portal type of single-story factory buildings (warehouses) with a fire resistance level of level 2. The inter-column supports of the rigid frame (according to the provisions of Article 3.1.1 of the Steel Structure Fire Protection Code "Note: 2" the fire resistance limit can be 2.0 hours) are also made of intumescent fire retardant paint (thin type). Because the word "unsuitable" is used in paragraph 2 of Article 4.1.3 of the Steel Structure Fire Protection Code, which means that it must be done when conditions permit, and it may not be done when conditions do not allow it. And round steel is sprayed with several centimeters of non-expandive fireproofing It is too difficult to paint (thick type) and it is "not allowed by conditions", so "it does not need to be done", which means that the rule "it is not appropriate to use intumescent fire retardant coatings" does not need to be implemented. For the inter-column supports of portal frames with a fire resistance level of Class I (the fire resistance limit is 3.0 hours; when it is a single-story factory building, the fire resistance limit can be stated in Article 3.1.1 of the Steel Structure Fire Protection Code "Note: 2") 2.5 hours), it is recommended to use angle steel support and non-expandive fire retardant paint (thick type).
5 结论
(1) In most cases, fire protection measures should be taken for steel structural components because their fire resistance limit without fire protection is lower than the design fire resistance limit (ie Td ≤ Tm, Td is the critical temperature, which means that steel components are exposed to fire The temperature when the function reaches the limit state of its fire resistance bearing capacity; Tm is the highest temperature of the non-fire protection component within the design fire resistance limit tm time). Only in rare cases, that is, when the load ratio is very small (equivalent to a large cross-section), the cross-sectional shape coefficient is small, and the fire resistance limit is small, Td>Tm will occur, and fire protection is not required.
(2) Steel columns, rigid ties between columns (XG) and shaped steel column supports (ZC) should be protected with non-intumescent fire retardant paint (thick type) (expandable fire retardant paint can be used when the building fire resistance level is level 4). The thickness should be determined through calculation, generally 15~40mm; it is recommended to use intumescent fire retardant coating (thin) for protection between round steel column supports (ZC), and the thickness is generally 1.5~7mm.
(3) Roof steel beams, roof ties (XG) and shaped steel roof supports (SC) can be protected by non-intumescent fire retardant paint (thick type) or intumescent fire retardant paint (thin type); round steel house Cover supports (SC) are protected with intumescent fire retardant paint (thin type). The thickness of the steel beam fire retardant coating should be determined through calculation, and the thickness of the non-intumescent fire retardant coating (thick type) should not be less than 15mm, and the thickness of the intumescent fire retardant coating (thin type) should not be less than 1.5mm.
(4) Since the design fire resistance limit of steel beams is smaller than the design fire resistance limit of steel columns, the thickness of the protective layer of fire retardant coating on steel beams is generally smaller than the thickness of the protective layer of fire retardant coating on steel columns.
(5) When the wind load is small, the height and span of the door rigid structure are small, and the number of inter-column supports (ZC) is large, the thickness of the fire protection layer of the inter-column supports (ZC) and inter-column ties (XG) is generally smaller than that of the steel The thickness of the fire protection layer of columns, roof supports (SC) and roof ties (XG) is generally smaller than the thickness of the fire protection layer of steel beams. It is safer to use the same fire protection method as that of steel columns and the same fire protection of roof supports (SC) and roof ties (XG) as that of steel beams. When the wind load is large, the height and span of the door rigid structure are large, and the number of column supports is small, the column supports (ZC), column ties (XG), roof supports (SC), and roof ties ( XG) fire retardant coating protective layer thickness should be determined by calculation.